The Convergence of AI and Cryptocurrency: A Trend Driven by Wright's Law
TLDR:
- AI and Cryptocurrency Convergence: AI and cryptocurrency are integrating, driven by Wright's Law, which predicts cost reductions as production scales. This convergence is poised to revolutionize finance, healthcare, supply chain management, and the energy sector.
- Benefits: The merger promises advances across various industries, including AI-driven financial services, secure patient data in healthcare, optimized logistics, and energy distribution.
- Autonomous Economic Agents (AEAs): These AI-driven agents will execute transactions and manage digital assets autonomously on blockchain networks, creating new economic models.
- Future Trends: Expect increased adoption, transformations across industries, enhanced privacy, and the democratization of AI through decentralized platforms.
- Wright's Law Influence: As production scales, costs will decrease, accelerating the adoption and development of AI and cryptocurrency technologies.
Introduction
Imagine a world where financial transactions are not just secure and transparent, but also intelligent and adaptive. This isn't science fiction—it's the promise of the convergence between artificial intelligence (AI) and cryptocurrency. As these two groundbreaking technologies intertwine, they're set to reshape our digital landscape in ways we're only beginning to comprehend.
This article explores the exciting intersection of AI and cryptocurrency, examining how Wright's Law is driving their integration and what it means for our future. We'll delve into the benefits, challenges, and emerging trends that are defining this technological revolution.
Understanding the Convergence
Defining the Players
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These include learning, problem-solving, and pattern recognition1.
Cryptocurrency is a form of digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security and operates independently of central banks.
Wright's Law: The Engine of Progress
At the heart of this convergence lies Wright's Law, a principle that states for every cumulative doubling in production, costs decrease by a constant percentage. In the context of AI and cryptocurrency:
- As AI hardware production increases, costs fall, making AI more accessible.
- As blockchain networks process more transactions, the cost per transaction decreases, enhancing crypto viability.
- The more people use these technologies, the more efficient and cost-effective they become.
AI-Enhanced Cryptocurrency
- Market Analysis: AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data to identify trading opportunities and trends. For example, platforms like Numerai use AI to crowdsource hedge fund strategies.
- Fraud Detection: Machine learning models can spot unusual patterns in transactions. Chainalysis, a blockchain analysis company, uses AI to detect and prevent cryptocurrency fraud.
- Personalized Investment Strategies: AI can create tailored investment plans based on individual risk profiles. Platforms like Wealthfront are already using AI to optimize crypto portfolios.
Cryptocurrency Empowering AI
- Decentralized Infrastructure: Blockchain provides a secure, transparent framework for AI applications. SingularityNET, for instance, aims to create a decentralized marketplace for AI services.
- Data Integrity: The immutable nature of blockchain ensures the reliability of data used by AI systems. Projects like Ocean Protocol are working to create a decentralized data exchange to support AI development.
- Tokenization of AI: Crypto tokens can incentivize AI development and improvement. Fetch.ai is pioneering this approach, creating an ecosystem where AI agents can autonomously trade digital assets.
Benefits and Opportunities
The convergence of AI and cryptocurrency promises to revolutionize various industries:
- Finance: AI-driven financial services using cryptocurrencies could transform lending, insurance, and asset management. Imagine smart contracts that automatically adjust interest rates based on real-time market conditions.
- Healthcare: Blockchain could secure patient data while AI analyzes it to improve diagnoses and treatment plans. MedRec, an MIT project, is exploring this potential1.
- Supply Chain Management: AI-optimized logistics combined with blockchain-based tracking could dramatically increase efficiency and transparency. Walmart is already using blockchain to track food supply, and AI could further enhance this system.
- Energy Sector: AI could optimize energy distribution on decentralized grids, with transactions facilitated by cryptocurrencies. The Brooklyn Microgrid project is an early example of this concept in action.
Predictions and Future Trends
Increased Adoption:
As AI costs decrease, more individuals and institutions will embrace cryptocurrencies. AI-driven applications tailored for the crypto ecosystem, such as advanced trading bots and user-friendly interfaces, will become more widespread.
Transformations Across Industries:
The merger of AI and crypto is expected to significantly impact various sectors:
- Finance: Automated, AI-driven financial services using cryptocurrencies could revolutionize lending, insurance, and asset management.
- Healthcare: Blockchain could secure patient data, while AI analyzes it to improve diagnoses and treatment plans.
- Supply Chain Management: AI-optimized logistics combined with blockchain-based tracking could dramatically increase efficiency and transparency.
- Energy Sector: AI could optimize energy distribution on decentralized grids, with transactions facilitated by cryptocurrencies.
Enhanced Privacy and Security:
Advanced methods will protect data and enable new forms of collaboration.
a) Homomorphic Encryption:
This advanced cryptographic technique allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it first. In the context of AI and crypto:
- AI models can analyze encrypted data, maintaining privacy while still deriving insights.
- Financial institutions could process cryptocurrency transactions without exposing the underlying data.
- Secure multi-party computation becomes possible, allowing multiple parties to jointly compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private.
b) Zero-Knowledge Proofs:
This cryptographic method allows one party (the prover) to prove to another party (the verifier) that a statement is true without revealing any information beyond the validity of the statement itself. Applications in AI and crypto include:
- Verifying the integrity of AI model outputs without revealing the model's proprietary structure.
- Proving ownership or the right to use a cryptocurrency without revealing the actual balance or transaction history.
- Validating the correctness of complex computations in privacy-preserving machine learning.
c) Federated Learning:
This machine learning technique enables training AI models on decentralized data. When combined with blockchain:
- Multiple parties can collaboratively train AI models without sharing raw data.
- The blockchain can serve as an immutable ledger of model updates, ensuring transparency and auditability.
- Crypto tokens can incentivize high-quality data contributions to improve model performance.
d) Differential Privacy:
This statistical technique adds controlled noise to datasets, making it difficult to extract information about any specific individual. In the AI-crypto space:
- Blockchain networks can implement differentially private mechanisms to protect user transaction patterns.
- AI models can be trained on sensitive data with guaranteed privacy bounds.
- Cryptocurrency wallets can obscure transaction amounts while still allowing for network validation.
e) Secure Enclaves and Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs):
These hardware-based security solutions create isolated environments for processing sensitive data. In the context of AI and crypto:
- AI computations can be performed within secure enclaves, protecting both the model and the data it processes.
- Cryptocurrency wallets can leverage TEEs for secure key storage and transaction signing.
- Oracles, which provide external data to smart contracts, can use TEEs to ensure the integrity of the data they feed into blockchain networks.
f) Post-Quantum Cryptography:
As quantum computers threaten to break current cryptographic standards, both AI and crypto are pushing for quantum-resistant algorithms:
- Blockchain networks are exploring post-quantum cryptography to secure transactions against future quantum attacks.
- AI is being used to develop and test new quantum-resistant encryption methods.
- Hybrid classical-quantum cryptographic systems are being developed to provide long-term security for sensitive AI and financial data.
These privacy-enhancing technologies, combined with AI and crypto, are generating "privacy-by-design" systems. These advances protect user data and enable new collaboration and data sharing that were previously unattainable due to privacy concerns. More complex applications that balance data utility with strict privacy constraints could revolutionize healthcare, finance, and scientific research.
Autonomous Economic Agents:
New autonomous economic agents (AEAs) will make judgments and execute transactions on blockchain networks using predefined rules and real-time data analysis.
a) Definition and Core Concepts:
- AEAs are software agents that can operate independently, make economic decisions, and interact with other agents or humans within a blockchain ecosystem2.
- They combine AI capabilities (such as machine learning and natural language processing) with blockchain features (like smart contracts and tokenization).
- AEAs can own digital assets, enter into agreements, and perform tasks without direct human intervention.
b) Key Capabilities:
- Autonomous Decision Making: AEAs can analyze market conditions, assess risks, and make trading or investment decisions based on sophisticated AI algorithms.
- Smart Contract Interaction: They can automatically initiate, negotiate, and execute smart contracts on blockchain platforms.
- Data Analysis and Prediction: AEAs can process vast amounts of data to predict market trends, optimize resource allocation, or identify investment opportunities.
- Self-improvement: Through machine learning, AEAs can improve their performance over time, adapting to changing market conditions and refining their decision-making processes.
c) Potential Applications:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): AEAs could act as automated market makers, liquidity providers, or yield optimizers in DeFi protocols, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error.
- Supply Chain Management: Autonomous agents could manage inventory, negotiate prices, and execute orders across complex supply chains, optimizing for efficiency and cost.
- Energy Markets: In decentralized energy grids, AEAs could buy and sell energy on behalf of households or businesses, optimizing for cost and sustainability.
- Real Estate: AEAs could manage property rentals, handle maintenance requests, and even participate in fractional ownership markets.
- Personal Finance: Acting as AI-powered financial advisors, AEAs could manage individual investment portfolios, automatically rebalancing and executing trades based on the user's goals and risk tolerance.
These agents could transform economic interactions, create new markets, and challenge our understanding of economic systems as they become smarter and more ubiquitous. To address ethical, legal, and security concerns, their creation and execution must be managed carefully.
Democratization of AI:
Blockchain-based platforms could enable decentralized AI marketplaces where developers can sell their models for money.
a) Decentralized AI Marketplaces:
- Concept: These platforms would enable AI developers to publish their models, datasets, and algorithms on a blockchain-based marketplace.
- Tokenization: AI models and datasets could be tokenized, allowing for fractional ownership and more fluid trading of AI assets.
- Smart Contracts: Automated licensing and revenue sharing could be facilitated through smart contracts, ensuring fair compensation for developers.
- Examples: Projects like SingularityNET and Ocean Protocol are pioneering this concept, creating decentralized networks for AI services.
b) Incentivization and Collaboration:
- Reward Mechanisms: Cryptocurrency-based rewards could incentivize developers to create and improve AI models, fostering innovation.
- Collaborative Development: Blockchain could enable transparent, traceable collaboration on AI projects, with contributions rewarded through crypto tokens.
- Crowdsourcing: Decentralized platforms could facilitate the crowdsourcing of data and computing power, democratizing access to resources needed for AI development.
c) Accessibility and Inclusivity:
- Lowered Barriers to Entry: By providing access to pre-trained models and datasets, these platforms could enable smaller players and individuals to participate in AI development2.
- Global Participation: Blockchain's borderless nature could allow developers from anywhere in the world to contribute to and benefit from the AI ecosystem.
- Diverse Applications: Increased accessibility could lead to the development of AI solutions for niche or underserved markets.
d) Transparency and Trust:
- Auditable AI: Blockchain's immutability could provide a transparent record of an AI model's development history, enhancing trust and accountability.
- Verifiable Computations: Zero-knowledge proofs could be used to verify the results of AI computations without revealing the underlying data or model.
- Ethical AI: Transparent development processes could help in identifying and mitigating bias in AI models.
e) Decentralized Compute Power:
- Distributed Training: Blockchain could facilitate the creation of decentralized networks for AI model training, leveraging idle computing resources globally.
- Edge AI: Integration with IoT devices could enable decentralized, edge-based AI computations, enhancing privacy and reducing latency.
- Example: Projects like Golem Network and Oasis Labs aim to create a decentralized supercomputer that could be used for AI training and inference.
Challenges to Integration
Despite the promising outlook for the convergence of AI and cryptocurrency technologies, several significant challenges must be addressed for successful integration.
- Regulatory and Legal Concerns:
-
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The rapid evolution of both AI and crypto technologies often outpaces regulatory frameworks, creating uncertainty for businesses and investors. Also, different jurisdictions have varying approaches to regulating AI and cryptocurrencies, making global integration challenging.
- Securities Laws: There's ongoing debate about whether certain cryptocurrencies should be classified as securities, which could impact their integration with AI systems.
- AI Governance: As AI systems become more autonomous, questions arise about legal liability and accountability for AI-driven decisions in crypto markets.
- Ethical Considerations:
- AI Bias: Ensuring that AI systems operating in crypto markets are free from bias is crucial to maintaining fair and equitable financial systems.
- Transparency: The "black box" nature of some AI algorithms may conflict with the transparency ethos of many blockchain projects.
- Decentralization vs. Control: Balancing the decentralized nature of blockchain with the need for some level of control and governance in AI systems is a complex challenge.
- Market Volatility and Economic Impact:
- Economic Disruption: The automation of financial processes through AI and crypto could lead to job displacement in traditional finance sectors.
- Wealth Concentration: There are concerns that the combination of AI and crypto could exacerbate wealth inequality if not managed properly.
- User Adoption and Education:
- Complexity: The technical complexity of both AI and crypto can be a significant barrier to widespread adoption.
- User Experience: Creating user-friendly interfaces for AI-driven crypto applications that are accessible to non-technical users is challenging.
- Digital Literacy: There's a need for widespread education about both AI and crypto to ensure responsible use and adoption.
- Standardization and Interoperability:
- Lack of Standards: The absence of universal standards for AI-blockchain integration hampers interoperability and widespread adoption.
- Data Standardization: Ensuring that data used by AI systems across different blockchain networks is standardized and compatible is a significant challenge.
- Resistance from Traditional Systems:
- Banking Sector Resistance: Traditional financial institutions may resist the integration of AI and crypto due to perceived threats to their business models.
- Governmental Concerns: Some governments may be hesitant to embrace AI-crypto integration due to concerns about losing absolute control over monetary policy and financial systems.
New issues will develop that require constant attention and innovation. But overcoming these constraints could unlock AI-crypto integration's immense potential, making financial and technological systems more efficient, transparent, and accessible.
Technological Limitations:
These limitations span various aspects of both AI and blockchain technologies:
a) Scalability of Blockchain Technology:
- Transaction Throughput: Many blockchain networks, particularly public ones like Ethereum, face limitations in the number of transactions they can process per second. This can be a significant bottleneck for AI applications that require high-frequency, real-time interactions. The leading layer 1 solution thus far is the Solana blockchain.
- Block Size and Time: The size of blocks and the time taken to create new blocks can limit the amount of data that can be stored and processed on the blockchain, potentially constraining AI operations. Layer 2 solutions on Ethereum looks promising, but the highest security resides on the underlying Ethereum chain.
- Solutions: While solutions like Lightning Network for Bitcoin, single-slot finality (SSF) for Ethereum, and Solana incorporate Firedancer to address speed and scalability, their integration with AI systems presents additional complexities.
b) Algorithmic Bias in AI:
- Data Bias: AI models trained on biased data can perpetuate and amplify existing biases, which is particularly concerning in financial applications.
- Model Bias: The design of AI algorithms themselves can introduce biases, even with unbiased training data.
- Feedback Loops: In decentralized systems, biased AI models could create feedback loops that exacerbate inequalities or market inefficiencies.
c) Transparency and Explainability:
- Black Box AI: Many advanced AI models, particularly deep learning models, operate as "black boxes," making it difficult to understand their decision-making processes. This lack of transparency can be problematic in financial and legal contexts.
- Smart Contract Complexity: As smart contracts become more complex, potentially incorporating AI elements, ensuring their transparency and auditability becomes more challenging.
- Regulatory Compliance: The lack of explainability in AI models can make it difficult to comply with regulations that require transparency in decision-making processes.
d) Interoperability:
- Blockchain Interoperability: Different blockchain networks often can't communicate directly with each other, which can limit the potential of AI systems that need to operate across multiple chains.
- AI-Blockchain Integration: Standardizing the integration of AI models with blockchain networks is still an evolving field, with various competing approaches.
e) Energy Consumption:
- Proof of Work: Many blockchain networks, particularly those using Proof of Work consensus mechanisms, consume large amounts of energy. This can be at odds with the computational requirements of AI systems.
- AI Training: Training large AI models requires significant computational resources and energy, which can be challenging to reconcile with the decentralized nature of many blockchain networks.
- Sustainable Solutions: Expanding grid baseload with multiple sources of energy production and developing energy-efficient consensus mechanisms and AI training methods is crucial for the long-term sustainability.
f) Security and Privacy:
- Privacy-Preserving AI: Developing AI systems that can operate on encrypted data (using techniques like homomorphic encryption or secure multi-party computation) while maintaining the privacy guarantees of blockchain is technically challenging3.
- Quantum Resistance: Both blockchain cryptography and AI systems will need to evolve to resist potential attacks from quantum computers. AI developers who are currently integrating Web3 are confident AI solutions will secure the blockchain even beyond quantum computing.
g) Governance and Upgradeability:
- AI Model Updates: Updating AI models in a decentralized environment while maintaining consensus and security is a complex challenge.
- Blockchain Upgrades: Implementing upgrades to blockchain protocols that may affect AI operations requires careful coordination.
- Decentralized Governance: Creating effective governance mechanisms for AI-driven decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) is a novel area that will require test environments to perfect.
The Role of Wright's Law in AI-Crypto Convergence
Wright's Law, which states that for every cumulative doubling in production, costs will fall by a constant percentage, is central to the AI-crypto convergence:
- AI Hardware Costs: As production of AI-specific hardware (like GPUs and TPUs) increases, costs are expected to decrease, making AI more accessible.
- Blockchain Scalability: As blockchain networks process more transactions, the cost per transaction is likely to decrease, making crypto more viable for everyday use.
- Learning Curve: As more people use AI and crypto technologies, their collective knowledge and efficiency will improve, further driving adoption.
Conclusion
AI-crypto convergence offers great potential for innovation and social change, giving great opportunities for anyone willing to embrace this new paradigm. By combining these technologies and Wright's Law's cost-cutting power, new applications and efficiencies will arise, changing how we interact with digital assets and intelligent systems.
Whether you're a developer, investor, or simply a curious observer, now is the time to engage with these technologies and help shape the digital economy of tomorrow.
FAQs
How does Wright's Law apply to AI and cryptocurrency convergence?
Wright's Law predicts that for every cumulative doubling in production, costs fall by a constant percentage. This principle suggests that as AI and cryptocurrency technologies scale, their costs will decrease, enabling broader development and adoption.
What are the benefits of AI-enhanced cryptocurrency trading?
AI enhances cryptocurrency trading by analyzing vast datasets to identify trading opportunities and trends, providing sentiment analysis, detecting fraud, and creating personalized investment strategies, all of which will become more accessible as AI costs decrease.
How does blockchain technology support AI development?
Blockchain offers a decentralized framework for AI applications, ensures data integrity, facilitates tokenization for AI development incentives, and enables the secure sharing of AI models and datasets, making data management more efficient and cost-effective.
What future trends can we expect from AI and cryptocurrency integration?
Future trends include increased adoption of cryptocurrencies, transformations across industries such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management, enhanced privacy and security, AI-powered autonomous agents, and the democratization of AI through blockchain-based platforms.
Donald Trump's Crypto Evolution: Implications for Bitcoin, Crypto, and the 2024 Presidential Election
TLDR
Donald Trump's evolving stance on cryptocurrency from skepticism to advocacy is reshaping the 2024 presidential race. His new pro-crypto position taps into a growing voter base, aligns with Republican free-market principles, and introduces significant potential changes to financial regulations in the U.S.
From Skeptic to Champion: A Calculated Pivot
Donald Trump's recent embrace of cryptocurrency and digital property rights marks a seismic shift in his stance, with far-reaching implications for the 2024 presidential race and the future of digital asset regulation in the US. This dramatic pivot from skepticism to advocacy highlights cryptocurrencies' growing political and economic importance and raises important questions about the future of American financial policy.
During his presidency, Trump was openly skeptical of digital assets, calling them "a scam" and "a disaster waiting to happen." However, his position has dramatically changed in the lead-up to the 2024 election. The Republican Party platform, which Trump edited, now strongly supports cryptocurrency and opposes central bank digital currencies (CBDCs).
Key Moments of Change
Trump's recent speeches and policy proposals underscore his new support for the crypto industry. Notably, Trump’s speech at the Bitcoin 2024 conference in Nashville highlighted his commitment to ending what he called the "unlawful and un-American crypto crackdown." This shift indicates a strategic move to align with the growing influence of the crypto community.
Factors Behind Trump's Strategic Pivot
- Appealing to a Growing Demographic:
The crypto community represents a rapidly expanding and influential voter demographic. By embracing bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, Trump aims to capture the support of crypto holders and enthusiasts, potentially swaying votes in his favor.
- Aligning with Republican Economic Principles:
The pro-crypto stance aligns perfectly with the Republican Party's emphasis on deregulation and free-market principles. By promising to end the "unlawful and un-American crypto crackdown," Trump appeals to the core tenets of his party's economic ideology. - Unlocking a New Fundraising Avenue:
The crypto industry has become a significant source of campaign contributions. Trump's campaign has reportedly received $25 million in cryptocurrency donations over two months, highlighting the lucrative potential of this fundraising stream. - Positioning as a Pro-Innovation Candidate:
By championing Bitcoin and digital property rights, Trump aims to portray himself as a forward-thinking leader who embraces technological innovation and understands the potential of the digital economy. - Tapping into Anti-CBDC Sentiment:
Trump's staunch opposition to Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) resonates with conservative anxieties about government surveillance and control over personal finances. This stance positions him as a defender of individual liberty and financial privacy. - Global Competitiveness:
By promising to make the U.S. a "Bitcoin superpower," Trump frames crypto adoption as a matter of national competitiveness. This could influence discussions about America's role in the global financial system.
The Implications of a Crypto-Educated Trump Presidency
Should Trump win the 2024 election, his crypto-friendly policies could have far-reaching consequences:
Regulatory Overhaul
If Trump wins the 2024 presidential election, his administration could push for a comprehensive overhaul of crypto regulations. This might include dismantling existing restrictions and appointing crypto-friendly individuals to key regulatory positions, potentially transforming the financial system.
Bitcoin as a Strategic Asset
Trump has hinted at the possibility of embracing Bitcoin as a strategic asset, potentially challenging the dominance of the US dollar in global finance. This could have significant geopolitical ramifications and reshape the international monetary system. Expanding on this point:
a) Challenging Dollar Hegemony:
By embracing Bitcoin as a strategic asset, the U.S. could be signaling a willingness to diversify its monetary strategy beyond the traditional reliance on the U.S. dollar. This could:
- Reduce the country's vulnerability to potential weaponization of the dollar-based financial system by adversaries. Provide an alternative to the SWIFT system for international transactions, potentially reducing U.S. ability to impose financial sanctions. Encourage other nations to consider similar strategies, potentially accelerating the shift away from dollar dominance.
b) Economic Implications:
The U.S. could potentially benefit from early large-scale adoption of Bitcoin, especially if its value continues to appreciate over time. However, this could also introduce new volatility into the national economic strategy, given Bitcoin's historical price fluctuations. It might lead to a reevaluation of how national wealth and economic power are measured and projected globally.
c) Geopolitical Power Dynamics:
Nations with significant Bitcoin mining operations (like China) could see their geopolitical influence shift. Countries with abundant renewable energy sources could gain strategic importance as ideal locations for Bitcoin mining. The move could be seen as a counter to China's development of the digital yuan, potentially sparking a "crypto race" among global powers.
d) International Monetary System Reshaping:
A U.S. embrace of Bitcoin could accelerate the development of a multi-polar currency world, where no single national currency dominates. It could lead to the creation of new international financial institutions and governance structures to manage a global financial system where cryptocurrencies play a major role. The IMF and World Bank might need to adapt their policies and operations to account for the growing importance of decentralized digital currencies.
e) Technological Sovereignty:
Embracing Bitcoin could spur increased investment in blockchain technology and cryptocurrency infrastructure within the U.S. This could help ensure that the U.S. remains at the forefront of financial technology innovation.
f) Global Trade Dynamics:
Bitcoin as a strategic asset could facilitate new forms of international trade settlement, potentially reducing reliance on traditional currency exchanges. It might enable easier trade with countries currently facing U.S. sanctions, which could be seen as both a benefit and a drawback, depending on the perspective.
g) Domestic Political Implications:
Such a move could face significant opposition from traditional financial institutions and some political factions. It might require a massive public education campaign to explain the strategy to the American public.
h) Cybersecurity Implications:
Elevating Bitcoin to the status of a strategic asset would likely make it an even bigger target for cyberattacks, requiring robust national cybersecurity measures.
Protection of Digital Property Rights
Trump’s focus on digital property rights could lead to new legislation that strengthens ownership and control over digital assets. This would have significant implications for the broader cryptocurrency market, including NFTs and the metaverse.
Expanding on this point:
a) Legal Framework for Digital Assets:
A Trump administration might push for comprehensive legislation to define and protect digital property rights, potentially creating a clearer legal status for cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and other digital assets. This could include establishing standards for proving ownership, transferring digital assets, and resolving disputes over digital property.
b) Impact on NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens):
Stronger digital property rights could legitimize and boost the NFT market, providing greater legal certainty for creators, buyers, and sellers. It might lead to more mainstream adoption of NFTs in areas like art, music, real estate, and intellectual property rights management. There could be clearer guidelines on copyright and royalties for NFT creators, potentially revolutionizing how digital artists and content creators monetize their work.
c) Metaverse Implications:
Enhanced digital property rights could accelerate the development and adoption of metaverse platforms by providing a solid legal foundation for virtual property ownership. This might lead to increased investment in virtual real estate and digital assets within metaverse environments. It could also raise complex questions about jurisdiction and governance in virtual worlds.
d) Intellectual Property in the Digital Realm:
Strengthened digital property rights might necessitate updates to existing intellectual property laws to better accommodate the unique characteristics of digital assets. This could include new frameworks for managing and enforcing patents, trademarks, and copyrights in purely digital contexts.
e) Cross-Border Implications:
A strong stance on digital property rights in the U.S. could influence international norms and potentially lead to new global agreements on the treatment of digital assets. It might also create challenges in harmonizing U.S. digital property laws with those of other countries, potentially leading to complex international legal scenarios.
f) Impact on Digital Identity:
Enhanced digital property rights could intersect with developments in digital identity, potentially leading to new ways of verifying ownership and identity in the digital space. This might have implications for privacy and data ownership, with individuals potentially gaining more control over their personal data as a form of digital property.
g) Financial Services Innovation:
Clearer digital property rights could spur innovation in financial services, enabling new forms of collateralization using digital assets. This might lead to the development of more sophisticated DeFi (Decentralized Finance) products and services.
h) Challenges in Implementation:
Defining and enforcing digital property rights would likely face technical challenges, particularly in proving ownership and preventing fraud in a decentralized digital environment. There might be resistance from traditional institutions that benefit from the current, less-defined state of digital property rights.
i) Educational Needs:
A significant shift in digital property rights would likely necessitate widespread education initiatives to help the public and businesses understand and navigate the new digital landscape.
j) Impact on Traditional Property Rights:
The strengthening of digital property rights could lead to interesting intersections with traditional property law, potentially blurring the lines between physical and digital ownership in some areas.
Increased Adoption and Innovation
A pro-crypto regulatory environment could accelerate innovation and adoption within the United States, potentially positioning the country as a global leader in the digital economy.
Impact on Traditional Finance
How might a strong pro-crypto stance affect the traditional banking sector and the broader financial system? A strong pro-crypto stance under a potential Trump administration could have significant ripple effects throughout the traditional financial sector:
a) Banking Sector Disruption:
Traditional banks might face increased competition from crypto-native financial services. This could lead to:
- Pressure on banks to innovate and offer crypto-related services to remain competitive.
- Potential loss of market share in areas like international remittances and payment processing.
- Increased investment in blockchain technology by traditional banks to stay relevant.
b) Regulatory Arbitrage:
A more permissive regulatory environment for crypto could create opportunities for regulatory arbitrage, potentially undermining existing financial regulations and creating new systemic risks.
c) Shift in Investment Patterns:
Increased mainstream acceptance of cryptocurrencies could lead to a shift in investment patterns, with more institutional and retail investors allocating portions of their portfolios to digital assets. This could potentially reduce demand for traditional financial products and services.
d) Impact on Monetary Policy:
Widespread adoption of cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, could complicate the Federal Reserve's ability to implement monetary policy effectively. This could lead to:
- Reduced effectiveness of interest rate adjustments.
- Challenges in managing inflation and economic stability.
e) Financial Inclusion:
Increased access to crypto services could potentially improve financial inclusion, providing banking-like services to underserved populations. This could pressure traditional banks to improve their offerings for these demographics.
f) Cybersecurity Concerns:
A rapid shift towards crypto could expose the financial system to new types of cybersecurity risks, requiring significant investment in new security infrastructure and expertise.
g) International Financial Relations:
A strong pro-crypto stance by the U.S. could influence global financial dynamics, potentially challenging the dominance of the U.S. dollar in international trade and affecting relationships with countries that have stricter crypto regulations.
h) Market Volatility:
The inherent volatility of many cryptocurrencies could introduce new elements of instability into the broader financial system, particularly if they become more intertwined with traditional financial products.
i) Job Market Shifts:
There could be significant shifts in the financial job market, with increased demand for crypto and blockchain expertise, potentially at the expense of traditional banking roles.
These potential effects are significant, but they depend on legislation and crypto acceptance. Over time, the traditional financial industry may adapt, creating a hybrid system that combines crypto and traditional money.
Conclusion: A Defining Issue in 2024
Donald Trump's embrace of crypto advocacy marks a pivotal shift in the 2024 presidential race, underscoring the growing political and economic significance of digital assets. This evolution promises to be a defining issue, potentially reshaping U.S. financial regulation and policy.
While a crypto-friendly administration offers potential benefits, it also presents complex regulatory challenges in a rapidly evolving and volatile sector.
The outcome of this debate could significantly influence the future of American financial policy, making the 2024 election a crucial moment for the trajectory of cryptocurrency in the United States.
FAQs
How has Trump's stance on cryptocurrency changed over time?
Initially skeptical, calling crypto a "scam," Trump has now embraced it, editing the Republican platform to support cryptocurrency and oppose CBDCs.
What factors influenced Trump's new pro-crypto position?
Key factors include appealing to a growing crypto voter base, aligning with Republican deregulation principles, unlocking new fundraising avenues, and opposing CBDCs.
What could a crypto-friendly Trump presidency mean for the U.S.?
It could lead to regulatory overhauls, increased adoption and innovation, protection of digital property rights, and potentially significant geopolitical ramifications.
What challenges could arise from Trump's crypto stance?
Challenges include balancing innovation with consumer protection, international coordination, implementation hurdles, and potential impacts on traditional finance.
Maximizing Staking Rewards with Effective Strategies
Maximize Your Crypto Staking Rewards: Strategies for Higher Returns
Staking cryptocurrencies has become an increasingly popular way for investors to earn passive income by supporting blockchain networks. Users stake coins and tokens to secure blockchain networks and earn staking rewards in return. However, simply staking your coins is not enough – maximizing your staking rewards requires careful planning and strategic decision-making.

Understanding the Basics of Crypto Staking
Staking involves holding coins in a digital wallet for a fixed period of time to participate in blockchain operations. While benefiting from the possible organic growth in coin value, stakers also earn additional rewards, making it comparable to earning interest on an investment.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithms like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Leased Proof of Stake (LPoS) are used to randomly select validators to create new blocks based on their staked holdings.
How Does Staking Work?
It's not just about pressing the 'stake' button and waiting for profits to roll in. Staking runs on "Proof of Stake" (PoS) consensus algorithms and its many variants such as Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Leased Proof Of Stake (LPoS), etc. In PoS-based blockchains, validators are chosen randomly by the algorithm to create blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to 'stake' as collateral.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| PoS (Proof-of-Stake) | Validators are randomly selected to create blocks. |
| dPoS (Delegated-Proof-of-Stake) | Allows users to vote for 'node representatives' who can then take part in block creation. |
| LPoS (Leased-Proof-of-Stake) | Calculates odds based upon total staking amount and the time duration it has been staked. |
Why Stake?
Staking crypto offers several advantages. You can grow your holdings with minimal effort, benefiting from potential market returns. Stakers earn rewards by securing transaction validations and often participate in network upgrades and votes. Additionally, staking has less downtime risk compared to traditional mining.
- Ease of Earning: Grow your holdings with relatively lower effort.
- Taking Control: Have a say over network upgrades and developments.
- Downtime Risk: Experience lower downtime risk relative to traditional mining methods.
- Growth: Cryptocurrency holdings increase over time.
Importance of Research in Maximizing Staking Rewards
Every investor should primarily focus on researching for the right crypto asset. Not all cryptocurrencies offer staking opportunities. Therefore, it's key to identify which coins enable staking and offer high return-on-investment (ROI).
Each crypto-asset has unique performance histories, future developments, and community support, all affecting its value. Researching network rates, such as inflation and interest rates, provides insights into potential profits. Key factors include the chosen crypto-asset, network rates, market dynamics, and suitable staking platforms.
| Crypto Asset | Inflation Rate | Interest Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Ethereum 2.0 | 1-3% | 6% |
| POLKADOT (DOT) | 10% | 16% |
Strategic Selection of Profitable Cryptocurrencies for Staking
When selecting cryptocurrencies for staking, it is crucial to evaluate several key factors to maximize profitability while managing risks effectively. Here are some important considerations:
Annual Percentage Yield (APY)
The APY represents the potential annual returns you can earn by staking a particular cryptocurrency. Generally, a higher APY is more desirable, but it may also indicate higher risk. Compare the APYs across different cryptocurrencies to gauge their relative profitability:
| Crypto | APY |
|---|---|
| Cardano (ADA) | 5.5% |
| Solana (SOL) | 6.7% |
| Polkadot (DOT) | 14% |
While Polkadot offers a higher APY, it's essential to consider other factors like stability and project sustainability.
Stability and Project Sustainability
Evaluate the stability and long-term viability of the cryptocurrency project. A well-established project with a strong development team, active community, and real-world use cases is generally more desirable for staking. Unstable or speculative projects may offer higher APYs but carry higher risks of price volatility or project failure.[1]
Staking Requirements
Different cryptocurrencies have varying staking requirements, such as minimum holding amounts, specific wallets or hardware, or lockup periods. Ensure you can meet these requirements before committing to staking:
| Crypto | Staking Requirements |
|---|---|
| Ethereum (ETH) | 32 ETH, specific software |
| Tezos (XTZ) | 8,000 XTZ or delegation to a baker |
| Cosmos (ATOM) | Delegation to validators, no minimum |
Failing to meet the requirements may result in penalties or missed rewards.
Unstaking Penalties and Lockup Periods
Some cryptocurrencies impose penalties or lockup periods if you unstake (withdraw your stake) before a certain time. Consider your liquidity needs and the potential impact of these restrictions on your investment strategy.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make informed decisions about which cryptocurrencies to stake, balancing profitability with risk tolerance and investment goals. Diversifying your staking portfolio across multiple cryptocurrencies can also help mitigate risks.
Keys to Optimal Stake Pool Selection for Higher Returns
The first important factor is the performance of the pool. Always investigate how a specific stake pool has been performing in terms of distribution interruptions, variable rewards and inconsistent returns. While past performance is not a guarantee of future results, it does give some idea about its efficiency and reliability.
Another critical element to consider is the pool’s saturation level. Saturation represents how much total stake a single pool has acquired. If the pool has a high degree of saturation, there's a good chance that it may yield less return per unit stake. Therefore, it is advisable to join a moderately saturated yet promising pool for higher profitability.
- Pool Size: Although larger pools seem more promising due to their network stability, small pools often offer higher rewards because fewer people share them.
- Variable Fee: This is calculated as a percentage of all rewards earned by stakeholders. Pools with lower variable fees often provide better long-term profits.
- Pledge: It refers to the amount of personal cryptocurrency the pool's creator has put into their own pool (mostly for younger projects). A higher pledge amount typically indicates more commitment towards their own venture.
| Key Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Performance | Indicates efficiency and reliability based on past stats |
| Saturation Level | Reflects the total stake a pool has accrued |
| Pool Size | Greater size can mean more network stability but potentially lower individual rewards |
| Variable Fee | A percentage of all rewards, lower is usually better for long-term profits |
| Pledge | The pool creators' personal cryptocurrency put into the pool as a sign of commitment. |
Considering all these factors before staking your digital assets can allow you to optimize your investment strategy and maximize your returns. Start with detailed research and consider diversifying across different pools to manage risk effectively.
Best Practices for Risk Management in Crypto Staking
Staking in the crypto arena has the potential for high returns, yet just as with any other investment, it is critical to align strategies with best practices to mitigate risk. Understanding these can provide a greater level of security, protect your asset value and optimise your profits. Here are a few key steps you can adopt to manage risk effectively while staking.
Firstly, diversification is key. Spreading assets across more than one project diminishes the negative impact should one of these projects fail or has disruptions. Just as you wouldn't put all of your eggs in one basket when investing in traditional spheres such as stocks or real estate, the same principle applies.
- Research: Spend adequate time understanding the various projects on offer before deciding where to stake your tokens.
- Analyse Past Performance: This will give you an insight into project stability and future perspective.
- Select a Varied Portfolio: By selecting different types of products that offer different benefits or operate within various sectors, you enable spread risk.
Secondly, it's crucial to clearly understand the terms and conditions associated with each staking agreement. Some staking providers impose penalties for early withdrawal or switching between validators. Be sure to read through all terms thoroughly before committing your tokens into a staking contract.
| Terms | Definition |
|---|---|
| 'Lock up' Duration | Period after which your tokens are not redeemable. |
| Validator Fees | Costs incurred to validate a transaction; it is typically a percentage of the rewards earned by you. |
Lastly, ensure to safeguard your security keys. Staking on a centralized platform is unsecure, as others are in control of the wallet keys. With decentralized finance (DeFi) your stake and rewards are tied to the secret key only you have. The risk of DeFi is if keys are lost, it's almost impossible to recover the funds. Therefore, it's advised always to keep multiple copies of your keys and store them in different secure locations.
Implementing Advanced Strategies to Maximize Staking Profits
Staking has been rising in popularity as one of the best ways to earn passive income in the cryptocurrency sector. However, to take full advantage and maximize your profits, you should employ advanced staking strategies. Instead of simply contributing your assets to any available pool, make certain considerations to optimize returns.
Choosing a Gravitating Pool: Not all staking pools are equal across parameters like reliability, fees, and rewards distribution policies. Consider aspects such as the size of the pool (a larger one improves chances of being chosen for block validation), past performance (check if the pool has been consistently generating blocks), costs involved (transaction fees and commission that can eat into profits), and uptime (as frequent downtime can lower rewards).
Ongoing Monitoring & Reinvestment: A common mistake that participants make is 'set it and forget it'. This approach can potentially lead to decreased profits over time due to variable transaction fees or changes in validation selection probabilities. Having an ongoing monitoring system helps track a pool’s performance and take decisions such as reinvesting earned interest back into the staking pool or shifting assets to other more profitable pools.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Staking | Selecting a viable stake pool based on stringent parameters for optimized returns. |
| Ongoing Monitoring | Maintaining a vigil on rewards generation and related variables for proactive decision-making. |
| Reinvestment Strategy | Tactfully reinvesting earned interest to compound staking profits. |
Moreover, the use of staking calculators can also significantly enhance the decision-making process. These tools provide estimates of possible future earnings based on several factors like staking duration, amount to be staked, and annual yield. Employing such advanced strategies in your staking endeavors can ensure maximized returns and a steady stream of passive income. Remember that as much as staking is relatively less risky compared to trading, doing some due diligence is always worthwhile.
Future Outlook
implementing effective staking strategies is crucial for maximizing your rewards in the crypto space. By diversifying your assets, staying informed about market trends, and choosing reputable staking platforms, you can significantly increase your returns. Remember to always prioritize security and research before making any staking decisions. With the right approach and dedication, you can make the most out of your staking rewards and grow your crypto portfolio efficiently. Happy staking!
10 Steps You Need to Pick Winning Crypto Projects
The journey to identifying and investing in promising cryptocurrency projects demands more than just a superficial glance. Engaging deeply with the project’s fundamentals and aligning with the vibrant Web3 community is not just advisable; it's essential.
This guide introduces a 10-step action list designed to streamline the process of identifying and capitalizing on elite cryptocurrency projects, emphasizing the indispensable role of thorough due diligence and robust community engagement. Whether you're a seasoned investor or new to the blockchain world, grasping the core technology, the strategic vision of the team, and the economic principles governing the tokens through detailed analysis, all while engaging with the ongoing dialogue and innovation within the community, is essential.
Such immersion not only enriches your investment approach but also enhances your ability to discern between fleeting trends and genuinely transformative opportunities in the Web3 space.
Step 1: Define Your Investment Goals
Before diving into any cryptocurrency investment or building a crypto portfolio, clearly define your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline. For example:
- Short-term goals may focus on investing in new crypto projects, ICOs, or high volatility tokens for quick gains.
- Long-term goals may lean towards established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum with stable growth.
Step 2: Conduct Comprehensive Research
Research the crypto project thoroughly, including understanding the problem it addresses, its blockchain technology, roadmap, and whitepaper. A real-world example of this importance is the rise of Ethereum, which was backed by:
- A strong whitepaper outlining the development of smart contracts.
- A clear roadmap that revolutionized blockchain utilities like DeFi.
Step 3: Analyze Tokenomics
 Investigate the token's utility, total and circulating supply, and any deflationary mechanisms. For instance, projects like Binance Coin (BNB) have successfully implemented:
Investigate the token's utility, total and circulating supply, and any deflationary mechanisms. For instance, projects like Binance Coin (BNB) have successfully implemented:
- Token burns, which have historically benefited the token price and ecosystem growth.
- Deflationary mechanisms that reduce the token supply over time.
Ethereum's deflationary mechanism refers to the changes in its economic model that have led to a decrease in the overall supply of Ether (ETH), the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network. This shift occurred primarily due to two significant updates:
- The Merge: In September 2022, Ethereum transitioned from a Proof-of-Work (PoW) to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism with an event known as "The Merge". This drastically reduced the rate at which new ETH is created.
- EIP-1559: The Ethereum Improvement Proposal 1559, implemented in August 2021, introduced a transaction fee-burning mechanism. A portion of the transaction fees, instead of going to miners, is now "burned" or permanently removed from circulation. As a result of these updates, the number of ETH being burned in transaction fees often exceeds the number of new ETH being created for network rewards. This has led to periods where the supply of ETH decreases over time, hence the term "deflationary" as opposed to "inflationary," where the supply would be increasing.
Step 4: Assess the Development Team
Evaluate the credibility, expertise, and track record of the project's development team. Successful teams include the following qualities:
- Projects with teams that have previously created and sustained successful cryptocurrencies.
- A strong development team must have open and transparent communication in order to work cohesively and efficiently towards a goal while responding to community sentiment.
- Adaptability is key in the fast-paced world of technology, as teams must be able to quickly adjust to changing requirements, technologies, and priorities.

Step 5: Understand the Project's Market Niche
Determine how the crypto project compares to its competitors and its unique selling proposition (USP). For example, Solana offers:
- High throughput and low transaction costs, positioning it uniquely against other layer-1 solutions.
- A USP that addresses the scalability issues faced by other blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Step 6: Review Market Performance and Historical Data
Look at the token's price stability, market cap trends, and trading volume. This can help gauge the cryptocurrency market's sentiment and the project's viability. For instance:
- Observing patterns in similar projects like EVM Layer 2's could provide insights into market behavior and potential future performance.
- Analyzing historical crypto data can reveal trends and potential entry/exit points for investments.
Step 7: Gauge Community and Ecosystem Support
A vibrant, engaged community and a growing list of partnerships can indicate a healthy project ecosystem. For example:
- The strong community support and developer activity around Polkadot are significant indicators of its robust ecosystem.
- Projects with active social media presence, forums, and developer communities tend to have better long-term prospects.
Step 8: Stay Updated on Regulatory News
 Keeping abreast of regulatory developments is crucial, as seen with XRP, where regulatory news has significantly impacted its market performance. Ensure the crypto project:
Keeping abreast of regulatory developments is crucial, as seen with XRP, where regulatory news has significantly impacted its market performance. Ensure the crypto project:
- Complies with the laws of the jurisdictions it operates within.
- Provides clear answers to all inquiries, whether in a spirit of complicity or dissidence.
- Has a clear strategy to navigate regulatory challenges.
Step 9: Practice Risk Management
Diversify your cryptocurrency investments to manage risk effectively. Do not over-invest in any single project. Instead, spread your capital across various assets to mitigate potential losses. Crypto is subdividing into sub-set markets, and there is usually a strong lead project in each:
- Layer 1's
- Layer 2's
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) blockchains
- Cosmos ecosystem
- Solana ecosystem
- Meme coins
- Gaming
- DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks)
- Etc. There is usually a product lead in each category.
Step 10: Continuous Monitoring and Reassessment
Regularly monitor the crypto project's progress against its roadmap, updates from the team, and ongoing market conditions. Active engagement can help you decide when to adjust your cryptocurrency holdings, similar to how:
- Early Bitcoin adopters have had to reassess their investment after each halving and with the evolution of the crypto market.
- Successful crypto investors continuously reevaluate their portfolio based on changing market dynamics.
This action list provides a structured approach to investing in cryptocurrency projects and the new asset class, drawing from real-world examples that highlight the significance of each step. By following these steps, investors can enhance their decision-making process and potentially increase their chances of investing in successful projects that offer unique value propositions and potential for long-term growth.
The information contained herein is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice or recommendations for making any financial decisions. Your situation is unique, and you should always do your own research, consult with industry experts, and be wary of projects that sound too good to be true. This information may not be accurate or timely, and the author or Investopedia may receive compensation from offers that appear on this site.
Beyond Bitcoin Halving: The Future of Crypto Post-Halving.
TLDR
- Understanding the mechanism and historical influence of Bitcoin halving.
- Analyzing the anticipated effects of the 2024 Bitcoin halving on investment dynamics.
- Highlighting technological advancements and strategies relevant post-halving.
- Evaluating potential risks and formulating strategic responses for investors.
Introduction
Bitcoin, the pioneer of cryptocurrencies, has introduced a unique economic model characterized by periodic 'halving' events. These milestones are pivotal moments where the reward for mining new blocks is halved, thus reducing the rate at which new bitcoins are introduced into the system. As we approach the 2024 halving, understanding its implications is crucial for both seasoned investors and newcomers to the cryptocurrency space.
The halving mechanism is a key feature of Bitcoin's design, aimed at controlling the digital currency's long-term supply and inflation rate. By periodically reducing the mining reward, the protocol ensures that the total supply of Bitcoin will eventually reach its cap of 21 million coins, making it a truly scarce asset in the digital realm.
Historical Analysis of Bitcoin Halvings
Historically, Bitcoin halvings have been watershed events that significantly influence the cryptocurrency's price and market dynamics. Following the first halving in 2012 and the subsequent ones in 2016 and 2020, bull runs propelled Bitcoin to new all-time highs. These patterns underscore the potential market movements post-2024 halving, although past performance is not indicative of future behavior.
The impact of previous halvings can be attributed to the basic economic principles of supply and demand. As the supply of new Bitcoin decreases due to reduced mining rewards, scarcity increases, potentially driving up prices if demand remains strong or increases. This dynamic has been a key factor in shaping investor sentiment and market behavior around halving events.

Economic Implications of Bitcoin Halving
The halving events are designed to create scarcity, a fundamental economic principle that underpins Bitcoin's value proposition. As the reward for mining decreases, the scarcity of Bitcoin increases, which could potentially drive up its price, assuming demand remains strong or increases.
However, it's important to note that scarcity alone does not guarantee price appreciation. Other factors, such as global economic conditions, regulatory developments, and competition from other cryptocurrencies, also play a significant role in shaping Bitcoin's value. The halving event's impact on price can be amplified or dampened by these external factors.
Institutional and Retail Investment Trends Post-Halving
In the aftermath of the 2024 Bitcoin halving, both institutional and retail investors are expected to closely monitor the market dynamics and adapt their strategies accordingly. Historically, halvings have been catalysts for significant price movements, peaking about 6 months post-halving.
Institutional investors, such as hedge funds, family offices, and corporate treasuries, may view the post-halving period as an opportune time to accumulate Bitcoin holdings. With the reduced supply of new coins entering circulation, institutions should now perceive Bitcoin as truly a scarce asset with long-term value appreciation potential.
Furthermore, 2024 is an election year, and with more citizen awareness of digital assets, there should be more crypto-favorable politicians in this cycle. With stronger positive crypto representation, regulatory developments could pivot dramatically. Clear guidelines and oversight mechanisms could provide the necessary confidence and legitimacy for larger players to embrace digital assets as part of their portfolios.
On the retail side, the halving event itself and the subsequent market movements usually attract a new wave of individual investors seeking to capitalize on the potential for price appreciation. The largest marketing campaign for Bitcoin within retail markets is the price itself.
During the post-halving period, we can expect to see a surge in interest and participation from various investors, each with their own unique motivations and strategies. The interaction between institutional and retail demand will play a crucial role in shaping the market dynamics and could potentially drive the price of Bitcoin beyond 2024 and well into 2025.
Technological Advancements Post-Halving
Post-halving, we can expect continued advancements in blockchain technology, enhancing transaction efficiency and security. These innovations will be crucial for Bitcoin to scale effectively and maintain its position at the forefront of the cryptocurrency market.
One of the most anticipated developments is the Lightning Network, a second-layer scaling solution that enables near-instant and low-cost transactions. The implementation of the Lightning Network could potentially address scalability issues and facilitate Bitcoin's wider adoption as a medium of exchange for everyday transactions.

Regulatory and Legal Landscape
In 2022, President Biden signed an executive order directing federal agencies to develop a comprehensive regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies. This move signaled the administration's recognition of the growing importance of digital assets and the need for a cohesive regulatory approach.
The SEC has taken a firm stance on classifying certain cryptocurrencies as securities, subjecting them to stringent disclosure and registration requirements. This approach supposedly aims to protect investors from fraudulent practices and ensure transparency in the crypto market. However, some industry players argue that excessive regulation stifles positive innovations and places undo limitations on blockchain technology.
On the other hand, the CFTC has been more accommodating towards cryptocurrencies, recognizing them as commodities and allowing the trading of Bitcoin and Ethereum futures on regulated exchanges. This stance has provided a degree of freedom for digital assets and facilitated their integration into traditional financial markets.
After the 2024 Bitcoin halving, the regulatory landscape in the United States will play a crucial role in shaping market sentiment and investor confidence. The current overly restrictive measures hinder adoption and dampen market enthusiasm.
The United States and other major economies should strive to implement balanced and innovative cryptocurrency regulations. Yes, regulations should aim to protect consumers and prevent illicit activities, yet they must foster innovation and allow the cryptocurrency industry to thrive. The ongoing efforts by various government agencies to establish clear guidelines and oversight mechanisms suggest that the United States is slowly moving towards a more comprehensive regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies. However, the specific details and the extent of regulations will ultimately determine the level of adoption and integration of digital assets into the traditional financial system.
Global Economic Factors Influencing Bitcoin's Trajectory
Global economic conditions, such as inflation rates, monetary policy changes, and economic downturns, play a significant role in shaping Bitcoin's attractiveness as an alternative investment. As a non-sovereign asset, Bitcoin has the potential to act as a hedge against fiat currency devaluation.
In times of economic uncertainty or high inflation, investors may turn to Bitcoin as a store of value, driving up demand and potentially contributing to price appreciation. Conversely, during periods of economic stability and low inflation, most investors treat Bitcoin similarly to a tech stock innovation, which could push the asset to the top of the S-curve faster than most tech adoption curves of the past.
Increasing Competitiveness in Bitcoin Mining
The Bitcoin mining landscape is becoming fiercely competitive, pushing miners to continually innovate and seek out the most efficient and cost-effective energy solutions. This drive for efficiency is a response to decreasing block rewards and a necessity in a maturing market where operational margins can be thin.
As mining difficulty increases and rewards decrease, miners will need to leverage the latest hardware and energy-efficient mining techniques to remain profitable. This competitive environment may lead to further consolidation, with larger mining operations potentially dominating the market, raising concerns about centralization.
Strategic Investment Approaches
Investors looking to leverage the halving event should consider diversifying their portfolios to include Bitcoin if they have not already. A strategic approach would involve balancing the potential high rewards against the volatility and risks inherent in cryptocurrency investments.
One common strategy is to employ dollar-cost averaging, which involves investing a fixed amount at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions. This approach can help mitigate the impact of price fluctuations and potentially lower the overall investment cost over time.
The Role of Bitcoin ETFs and Financial Products
The emergence of Bitcoin ETFs has made it easier for individuals to invest in Bitcoin without dealing with the technical challenges of handling cryptocurrencies directly. These financial products will likely expand, offering more options and potentially driving further adoption.
Bitcoin ETFs provide a regulated and convenient way for institutional and retail investors to gain exposure to the cryptocurrency market. Now, savvy investors are focused on other digital assets, such as Ethereum, gaining approval for ETF implementation.
Future of Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Ecosystem
Looking ahead, Bitcoin is poised to remain a significant player in the financial landscape. Its integration into broader financial systems, combined with the maturation of blockchain technologies, suggests a promising future.
As the world becomes increasingly digitized, the demand for decentralized, secure, and transparent financial systems will grow. Bitcoin, with its established network and first-mover advantage, will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of digital finance, provided it continues to evolve and address scalability, transaction speed, and transaction cost issues.
Conclusion
As the 2024 Bitcoin halving approaches, the cryptocurrency community stands at a crossroads that could define the future trajectory of Bitcoin and its underlying technology. For investors, staying informed and adaptable will be key to navigating this exciting yet challenging market.
By understanding the potential impacts of the halving on market dynamics, regulatory developments, and investment trends, investors can make more informed decisions and position themselves accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Bitcoin halving?
Bitcoin halving is an event that halves the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. It occurs once every 210,000 blocks, roughly every four years, reducing the block reward given to miners for processing transactions. The next halving is expected in 2024, where the reward will decrease from 6.25 to 3.125 BTC.
The halving mechanism is a crucial aspect of Bitcoin's design, aimed at controlling the digital currency's long-term supply and inflation rate. By periodically reducing the mining reward, the protocol ensures that the total supply of Bitcoin will eventually reach its cap of 21 million coins, making it a truly scarce asset in the digital realm.
Why does Bitcoin halving affect the price?
Bitcoin halving affects the price due to the basic economic principle of supply and demand. If the rate of new supply (i.e., the mining of new Bitcoin) decreases, and demand remains constant or increases, the price is likely to rise. Historically, each halving has been followed by a bull run in the Bitcoin market, although past performance is not indicative of future results.
Can Bitcoin halving lead to increased market volatility?
Yes, Bitcoin halving can lead to increased market volatility. This volatility typically arises from speculative trading and investor expectations leading up to and following the halving event. Investors often adjust their positions based on their predictions of how the halving will impact Bitcoin's price, contributing to price fluctuations.
Additionally, the decreased mining rewards post-halving may lead to a temporary reduction in the network's overall computing power, as some miners might find it unprofitable to continue operations. This temporary decrease in network security could contribute to short-term price volatility.
How should investors prepare for Bitcoin halving?
Investors should consider reviewing their investment strategies and possibly diversifying their
2024's Guide to Risk Management in Staking Digital Assets
Introduction
Staking digital assets is an increasingly popular activity in the cryptocurrency world. It involves holding funds in a cryptocurrency wallet to support blockchain operations while earning rewards. But as the industry grows, understanding and implementing effective risk management strategies becomes crucial to safeguarding investments and maximizing returns.
The Allure and Risks of Staking Digital Assets
Staking offers attractive rewards but comes with inherent risks. Understanding these risks is essential for effective management. Key risks include:
- Volatility Risk: The value of staked digital assets and rewards can fluctuate significantly due to market volatility.
- Security Risk: Staked assets face threats like hacking and blockchain vulnerabilities.
- Network Risks: Events such as congestion, upgrades, or hard forks can impact staking performance.
- Liquidity Risks: Difficulty in liquidating holdings quickly if needed.
Mitigating Risks in Digital Asset Staking
Adopting risk management strategies is vital to protect against losses and secure long-term profitability.
- Diversification of Assets: Spread stakes across multiple networks to reduce the risks inherent in any single one.
- Utilizing Insurance Products: Protect against losses from security breaches and other staking-specific risks.
- Active Participation in Governance: Influence network decisions and stay informed about potential risks.
- Continuous Risk Monitoring: Regularly assess risks to proactively address vulnerabilities.
- Setting Risk Tolerance Levels: Determine acceptable risk levels based on potential impact and personal risk tolerance.
Case Studies: Risk Management in Action
Diversification Benefits and Risks
Diversification is a cornerstone strategy in risk management. By spreading investments across various digital assets, blockchain networks, and even different forms of cryptocurrencies like stablecoins or Ethereum, investors can reduce their exposure to the failure or underperformance of a single asset.
However, diversification carries its own set of risks. The most prominent is the dilution of rewards. When assets are spread thin across multiple platforms, the potential gains from any one investment are reduced. Moreover, managing a diversified portfolio requires more time and expertise, especially in understanding the nuances of each asset class. Investors should also be wary of over-diversification, where the sheer number of investments makes effective monitoring challenging, potentially leading to suboptimal decisions.
Insurance Products
As digital asset staking becomes more mainstream, insurance products have emerged to mitigate specific risks associated with this investment method. These products offer protection against a range of events, including security breaches, custodial risks, and even smart contract failures.
However, investors must exercise due diligence when choosing insurance products. It's crucial to carefully examine the terms and conditions of each policy, understanding what is covered and what isn't. Premium costs should be weighed against the potential benefits, keeping in mind that insurance should complement, not replace, other risk management strategies. Furthermore, the reputation and financial stability of the insurance provider are essential considerations, as these factors impact the likelihood of a successful claim settlement in case of an adverse event.
Future Trends in Staking Risk Management
The future of staking risk management is poised to be shaped by several emerging trends and innovations, offering new approaches to handling the inherent risks of staking digital assets.
- The Rise of Staking Pools: Staking pools, where investors combine resources to increase reward chances, democratize reward distribution, allowing even small-scale investors to benefit. However, they pose questions about decentralization and the balance between accessibility and control.
- Derivative Staking: This trend involves creating financial products linked to staked assets. Derivative staking allows investors to receive a derivative token in return for staked tokens, providing liquidity for assets usually locked up during staking periods【25†source】.
- Cross-chain Staking: The emergence of blockchain interoperability has led to the concept of cross-chain staking. This allows investors to stake coins on one blockchain and use them in another, offering greater flexibility and opportunity.
- Eth2 and Shard Chains: The Eth2 upgrade and the introduction of shard chains are set to enhance the scalability of the Ethereum network, potentially impacting staking strategies and returns significantly.
- Liquid Staking: Addressing liquidity issues, liquid staking allows for the generation of a liquid, tradable representation of staked assets, combining the benefits of staking rewards and liquidity.
- Decentralized Staking as a Service (DSaaS): DSaaS aims to simplify staking by providing services directly on the blockchain, enhancing security, and fostering decentralization by minimizing the risks associated with centralized staking pools.
- Privacy-preserving Staking: Addressing growing privacy concerns, this innovation offers staking methods that protect users' identities and transaction histories, making staking more attractive for privacy-conscious investors.
- Staking-as-a-Service Platforms: These platforms simplify the staking process, handle technical requirements, and make staking accessible to a broader range of investors.
These trends highlight the evolving landscape of staking and the continuous need for robust risk management strategies. As the ecosystem matures, these innovations will likely play a significant role in shaping the future of staking in the digital asset space.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways in Staking Risk Management
Proactive risk management is pivotal in the evolving landscape of staking digital assets. As the ecosystem diversifies and becomes more complex, the importance of robust risk management strategies becomes paramount. These strategies are not just about mitigating risks but also about seizing opportunities in a way that aligns with individual risk profiles.
- Adaptability is Key: The staking ecosystem is dynamic. Effective risk management requires adaptability to new trends, regulatory changes, and technological advancements.
- Balance in Diversification: While diversification is crucial, it must be balanced to avoid over-diversification, which can dilute potential rewards and complicate portfolio management.
- Informed Decision-Making: Continuous education and staying informed about market developments, regulatory changes, and innovative risk management tools are vital for making well-informed decisions.
- Integration of Traditional and Innovative Approaches: Combining traditional finance's risk management practices with innovative approaches specific to digital assets can provide a comprehensive risk management framework.
- Importance of Governance Participation: Active participation in governance can influence network decisions and help in staying ahead of potential risks.
- Embracing Technology for Risk Management: Leveraging technology, like advanced analytics and automated tools, can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of risk management strategies.
- Privacy and Security: With the rise of privacy-preserving staking and DSaaS, investors can enjoy both security and privacy benefits, enhancing the appeal of staking.
- Regulatory Compliance: Staying compliant with evolving regulations is crucial for risk mitigation and to maintain investor confidence.
Investors who embrace risk management practices are better positioned to navigate the complexities of digital asset staking for sustainable growth and profitability.
Implementing risk management practices allows investors to protect their investments and minimize potential losses in the volatile and rapidly changing digital asset-staking market. By diversifying their staking portfolios, setting clear investment goals, and implementing stop-loss strategies, investors can lower their overall risk exposure while maximizing potential returns.
Additionally, conducting thorough research and due diligence on potential staking assets and platforms can help investors identify reputable and trustworthy opportunities, reducing the risk of fraud or scams. Engaging with experienced professionals and leveraging technology tools such as analytics and monitoring can also provide valuable insights to inform sound investment decisions.
By proactively managing risk, investors can position themselves for sustained growth and profitability in the digital asset staking space, effectively navigating market fluctuations and regulatory changes to capitalize on emerging opportunities. Ultimately, integrating risk management practices into their investment strategies can help investors achieve long-term success Alpha Stake is here to provide guidance services for those who want to engage in the crypto investing experience.
FAQs
What are the Main Risks in Staking?
The primary risks include volatility, security, network, and liquidity risks.
How Can Investors Mitigate Volatility Risk?
By diversifying portfolios, using hedging tools, and actively monitoring market trends.
What Should Investors Know About Regulatory Considerations?
It's important to stay informed about evolving regulations and comply with the latest compliance requirements.
Staking Showdown: Liquid Staking Protocols To Watch in the 2024

Introduction
As the world of cryptocurrencies continues to evolve, new and innovative solutions are developed to address the challenges that arise. One such solution that has captured the attention of crypto enthusiasts is liquid staking. In this article, we'll explore the benefits of Liquid Staking in 2024 and how it is transforming the digital asset management landscape.
Staking is a way of pledging valuable tokens to a blockchain to ensure its security and efficiency. Tokens that are staked, locked, to the blockchain provide liquidity and speed for transactions and pledgers guarantee themselves or their chosen transactions validator will abide by the protocol rules or risk losing a large percentage of their staked tokens, called "Slashing". Liquid staking represents a novel approach within the realm of cryptocurrency staking, by enabling staked assets to serve as collateral for generating liquidity. In return for staking, when a user stake their assets, they receive a wrapped version of that token that is equal or close to equal in value to the original token. Some protocols even allow additional staking of the wrapped token for additional staking yields. This feature is particularly advantageous for those reluctant to engage in long-term investments, preferring instead to utilize their staked assets for higher yields or utilize the derivative token for swing trading.
However, it is crucial to emphasize that some liquid staking necessitates long-term commitments and the original asset cannot be withdrawn within set time frames. Various blockchains permit derivative token creation via liquid staking, each with distinct rewards and risks. Consequently, selecting the appropriate blockchain for investment can be complex with many options to consider. In this context, platforms can assist by equipping users with the tools and resources required to make informed decisions concerning the blockchain on which to stake their assets. Liquid staking tokens are an auspicious development within the cryptocurrency, as it grants investors increased flexibility to trade while still enabling them to partake in the staking process. But first, let's dive into the basics!
The Magic of Liquid Staking in 2024
What is Liquid Staking?
Liquid staking is a novel approach to managing digital assets, particularly within proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchains. It allows users to stake their tokens and obtain a liquid, tradable token in exchange. This mechanism amplifies the staking experience by providing increased flexibility and accessibility to users. In traditional staking, assets are often locked for a predetermined period, limiting the investor’s ability to capitalize on market fluctuations. However, liquid staking resolves this issue by allowing participants to trade their staked assets as liquid tokens, granting them the freedom to respond to market changes and optimize their investment strategies.
This innovative solution democratizes access to the DeFi (Decentralized Finance) ecosystem for a broader audience. As more PoS blockchains choose to adopt the mechanism of staking vs liquid staking, users with varying investment capacities can participate in the staking process and earn rewards, thus adding more liquidity to the ecosystem.
Why Are Liquid Staking Tokens Gaining Traction?
The rapid growth of PoS blockchains has spurred a surge in demand for staking services. As more users recognize its potential, the benefits of Liquid Staking are becoming increasingly apparent. Some of the reasons for its rising popularity include greater flexibility, enhanced liquidity, and reduced risks, among others. With liquid staking, users can stake their tokens and still use them for other purposes, such as collateral for loans or trading on other platforms4. Unlike traditional staking, where investors can’t access their locked staked funds, liquid staking provides room for investors to be able to access their staked funds to make other investments. The liquid staked derivative enables less overall risk and empowerment to the end-user to stay involved with trading. When crypto exchanges, such as Binance and Coinbase, began accepting various forms of wrapped tokens that represented interest-bearing staked tokens, a higher level of comfortability arose from investors knowing they have options in multiple domains to liquidate and rebuy their liquid staking derivatives in return.
There's an undeniable appeal of popular liquid staking in the world of cryptocurrency. This innovative approach addresses traditional staking limitations and provides investors with more than they were getting from staking coins. Here are some key factors driving its sustained popularity:
Liquid staking significantly enhances liquidity, allowing investors to participate in staking without sacrificing their ability to respond to market shifts. Users can effortlessly trade liquid tokens and adjust their positions as needed, unlike traditional staking, where assets are locked for a fixed duration.
Liquid staking encourages inclusive participation by streamlining the often complex and capital-intensive staking process. This accessibility attracts a broader range of investors, fostering a diverse and thriving ecosystem, such as defi. Defi is a liquid staking derivative that allows yield plus market participation in a variety of ways the user sees fit.
As more users participate, the network's security increases, potentially resulting in higher staking rewards for stakeholders and further promoting liquid staking adoption.
The Benefits of Liquid Staking: An In-Depth Look
Flexibility: Staking vs Staking and Trading Combined
One of the primary benefits of Liquid Staking is the unprecedented flexibility it offers. By providing users with a liquid, tradable token in return for their staked assets, allows them to seamlessly move between staking and trading, maximizing their investment potential.
Flexibility is a crucial benefit of liquid staking. Traditional staking requires users to lock up their tokens for an extended period, which can limit their liquidity and flexibility. With liquid staking, users can enjoy the benefits of staking while retaining the flexibility to trade their tokens as needed. This can be particularly important in volatile market conditions when users may need to adjust their holdings quickly.
Liquid staking also allows users to combine staking and trading, which can offer significant advantages. When users stake their tokens, they typically earn rewards for holding them. However, these rewards are often limited to the specific cryptocurrency in which they are staked. With liquid staking, users can unlock the value of their staked tokens and use them to trade other cryptocurrencies or fiat currencies. This can allow them to earn additional profits and maximize their returns.
In addition to increased flexibility and the ability to combine staking and trading, liquid staking also offers other benefits. These include reduced risk, as users can liquidate their staked tokens quickly if market conditions change, and increased liquidity, as users can trade their tokens more easily than with traditional staking. Overall, liquid staking can be an excellent option for cryptocurrency holders who want to earn staking rewards while retaining the flexibility to trade their tokens as needed.
Liquidity: Unlocking the True Potential of Digital Assets
Another crucial benefit of liquid staking is the increased liquidity it brings. Staked assets are often locked, making them difficult to access or utilize. Liquid staking, on the other hand, enables users to freely trade or exchange their liquid tokens, thus ensuring their assets remain liquid and accessible at all times. Flexibility is a crucial benefit of liquid staking. Traditional staking requires users to lock up their tokens for an extended period, which can limit their liquidity and flexibility. With liquid staking, users can enjoy the benefits of staking while retaining the flexibility to trade their tokens as needed. This can be particularly important in volatile market conditions when users may need to adjust their holdings quickly. Since liquidity is a measure of the outside demand and supply of an asset, a deep market with ample liquidity is an indication of a healthy market. Liquidity in cryptocurrency lowers investment risk and assists in defining your exit strategy, making it simple to sell your ownership.
Increased liquidity in the cryptocurrency markets increases the resistance to manipulation by dishonest actors or coordinated groups. A liquid market is generally regarded as more stable with greater trading volume and decreasing volatility. High liquidity also aids in the analysis of trader behavior, providing insights into market trends and sentiment. This leads to greater price stability and reduced volatility, which are crucial for investors seeking to avoid abrupt price fluctuations that can result in losses.
Risk Mitigation: Reducing Exposure to Blockchain Market Fluctuations
Liquid staking is an innovative risk mitigation solution for investors in the volatile cryptocurrency market. By allowing users to stake their digital assets and receive tradeable liquid-staked derivative tokens in return, liquid staking offers trading flexibility and control over investments. This enables investors to better manage their exposure to market volatility, minimize potential losses, and enhance their overall investment experience. Liquid staking appeals to both risk-averse investors seeking to benefit from staking rewards without incurring significant losses and active traders who desire the ability to respond quickly to market shifts.
Standard staked crypto often limits investors' options for trading in and out the asset during clearly determined highs and low patterns. In contrast, liquid staking provides tradeable tokens representing staked assets, which can be quickly converted or sold off in response to market fluctuations. This feature not only makes staking more accessible but also enables investors or their representatives to actively manage their positions, resulting in a more investor-friendly and adaptive investment experience. As the crypto ecosystem continues to evolve, liquid staking is poised to become an increasingly important tool for investors seeking to optimize their risk management strategies.
Inclusivity: Bridging the Gap for Smaller Investors
The benefits of liquid staking are not just limited to large-scale investors; they also extend to smaller investors who may have limited capital. In traditional staking, substantial amounts of capital were often required to participate in the process, which effectively barred many smaller investors from taking part and earning rewards. This exclusivity created an uneven playing field, with only those who possessed significant financial resources able to benefit from staking.
Many liquid staking solutions enabled users with smaller amounts of tokens to participate. Users can stake under 32 ETH, for example, on Lido and participate in the eth liquid staking process earning fractions of ETH while holding valuable stETH. This democratization of access to staking opportunities fosters a more inclusive ecosystem, allowing a wider range of investors to reap the rewards of their investments. As a result, the barriers to entry are significantly reduced, and the cryptocurrency market becomes more accessible to a broader range of participants.
Simplifying Governance: A More Streamlined Experience
Liquid staking plays a crucial role in simplifying and streamlining governance within the blockchain ecosystem. By offering a more investor-friendly approach, liquid staking allows for a greater level of participation and engagement in the decision-making process, ultimately contributing to more effective governance.
Firstly, liquid staking democratizes the staking process by making it more accessible to a broader range of investors. Traditional staking often requires significant technical knowledge and considerable capital to participate effectively, which may deter potential investors. Liquid staking pools, on the other hand, simplify the process by allowing users to stake their assets and receive tradeable liquid tokens in return. These tokens can be easily managed by users, regardless of their technical expertise, thus enabling a larger number of stakeholders to participate in the governance process.
Moreover, liquid staking streamlines governance by facilitating faster and more efficient decision-making. Since liquid tokens are tradeable, users can actively participate in voting on network proposals and other governance-related matters without the need to unlock their staked assets. This flexibility encourages stakeholders to engage in the governance process more proactively, as they can continue to earn staking rewards while actively participating in the decision-making process.
Additionally, liquid staking promotes transparency in governance. As token holders actively trade and engage with liquid tokens, the network benefits from increased visibility of stakeholder preferences and opinions. This transparency leads to better-informed decisions and fosters trust within the community, ultimately contributing to a more robust governance structure.
A Practical Guide to Liquid Staking
Choosing the Right Liquid Staking Solution
Before engaging in the liquid staking market, it's important to evaluate the various solutions available and select one of the best liquid staking platforms that suit your needs. Factors include supported assets, staking rewards, and ease of use. Below are the top liquid staking platforms to watch in 2024. They are trusted to date because of their safety and liquidity.
| Platform | Supported Assets | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Lido | Ethereum, Terra, Solana | Liquid assets for staking, accessible across other decentralized protocols, attractive APYs. |
| Tempus | Yield-bearing Tokens | Decentralized fixed income, supports various yield-bearing tokens, no protocol fees. |
| Hubble | Solana, BTC, ETH, + others | Automatically earn a yield on collateral, use USDH stablecoin, and stake HBB for extra rewards. |
| Marinade | Solana | Stake SOL benefits from liquid staking, no un-staking period, and 400+ top validators. |
| Meta Pool | NEAR | Liquid staking for NEAR holders, stNEAR usable on other DeFi protocols, auto-compounded income. |
| Revault | Powered by Orbs L3 | Auto-rebalancing feature, integrates Orbs Layer-3 technology, maximizes APY. |
| Izumi | Uniswap V3 LP Tokens | Enhance liquidity mining rewards, non-custodial, fully decentralized, and supports Ethereum and Polygon. |
| Balancer Labs | Ethereum/Polygon | Various liquidity pools, programmable liquidity, and strong incentives for long-term liquidity provision. |
Honorable Mention Liquid Staking Platforms:
- Rocket Pool : Long-time liquid staking provider, however, only offers to liquid stake one asset, Ethereum.
- Strader: They only participate in liquid staking for a Layer 2 protocol, Polygon, and 2 blockchains that may be more obscure for new users, Binance Chain and Fantom.
- RockX: A global node operator whose staking strategies are focused on incorporating businesses into the blockchain ecosystem.
Precautions about Liquid Staking Protocols
Before staking crypto assets on liquid staking platforms, it is important to do due diligence on the provider of the liquid staking service. Your assets will contribute to the staking pool run by the protocol.
Some of the key precautions to consider include:
1. Smart contract risks: Like any decentralized finance (DeFi) application, liquid staking protocols rely on smart contracts. These contracts may be vulnerable to bugs, coding errors, or security exploits that could lead to loss of funds or disruptions in the staking process. It is crucial to choose liquid staking protocols with well-audited, battle-tested smart contracts and a strong track record of security.
2. Counterparty risks: Some liquid staking protocols involve the use of intermediaries or third-party platforms to facilitate staking and token exchanges. This introduces counterparty risks, as the protocol's success and security depend on the reliability of these third parties. Investors should thoroughly research and assess the reputation and trustworthiness of any involved intermediaries before committing to a liquid staking protocol.
3. Regulatory risks: The regulatory landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies and DeFi applications is continuously evolving, and future regulations could potentially impact liquid staking protocols. Investors should stay informed about regulatory developments and be prepared for the possibility of new rules or restrictions affecting their staking activities. Future regulations could potentially impact liquid staking protocols. For example, in 2022, the US SEC filed a lawsuit against Ripple Labs, alleging that the company had conducted an unregistered securities offering, which affected their offerings to the general public for over a decade. In 2024, the US Treasury Department proposed new rules that would require cryptocurrency exchanges to collect more information about their customers. Regulatory developments and competition from a government-sponsored Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) could potentially impact liquid staking protocols.
4. Market risks: Liquid staking does not eliminate the inherent market risks associated with cryptocurrencies. The value of liquid tokens is subject to fluctuations, and investors may still experience losses due to market volatility. It is vital to have a clear understanding of market dynamics and employ effective risk management strategies when participating in liquid staking. Not all proof-of-stake service provider who makes liquid staking possible may also have blockchain rules that make your stake of certain tokens illiquid (i.e. Cardano has > 25 days to unstake). Token transfers and delegation transactions may also incur fees ¹.
5. Slippage risks: When trading liquid tokens on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) or automated market makers (AMMs), investors may encounter slippage, which occurs when the executed price of a trade differs from the expected price. This can result in unfavorable trade outcomes, particularly during periods of high market volatility. To mitigate slippage risks, investors should consider using limit orders, trading on platforms with sufficient liquidity, and monitoring market conditions closely.
In conclusion, while liquid staking protocols offer many benefits, investors need to be aware of the potential risks and take appropriate precautions. By carefully evaluating smart contract security, counterparty reliability, regulatory developments, market risks, and slippage, investors can make more informed decisions and optimize their liquid staking experience.
One disadvantage liquid staking has over normal staking is smart contract risk. The wrapping of the staked token means an additional layer of smart contract interaction, which can potentially be exploited. Another potential risk is a divergence between the collateral value and the value of the wrapped token ²³.
Getting Started with Liquid Staking Protocols
Once you've carefully evaluated and selected a liquid staking platform that aligns with your investment goals, getting started with the process is usually quite simple. Here's a step-by-step process to help you stake your tokens:
1. **Create an account**: Sign up for an account on your chosen liquid staking platform. This may require providing your email address, creating a username and password, and completing any necessary verification steps.
2. **Connect your wallet**: Connect a compatible cryptocurrency wallet to the platform. This wallet should hold the tokens you intend to stake. Follow the platform's instructions to link your wallet securely, and ensure that you maintain control of your private keys.
3. **Stake your tokens**: Once your wallet is connected, navigate to the platform's staking section and select the cryptocurrency you wish to stake. Enter the amount you want to stake, and confirm the transaction. This may require approving a smart contract interaction or paying a transaction fee.
4. **Receive liquid tokens**: After successfully staking your tokens, the platform will issue you an equivalent amount of liquid tokens. These tokens represent your staked assets and can be freely traded or used in other DeFi applications.
5. **Monitor your staking rewards**: Keep an eye on your staking rewards and track their accrual over time. Liquid staking platforms often have user-friendly dashboards that display your rewards in real-time, making it easy to monitor your earnings.
6. **Trade or use your liquid tokens**: With your liquid tokens in hand, you can now take advantage of their flexibility. Trade them on supported exchanges, use them as collateral in lending protocols, or employ them in yield farming strategies to maximize your returns.
7. **Un-stake and redeem your original tokens**: When you're ready to un-stake your assets, exchange the liquid tokens back to the original tokens on the platform. Follow the platform's specific process to complete the un-staking and withdrawal of your tokens back to your wallet.
After conducting your diligence about each platform, you can choose which is best to stake your tokens, receive the corresponding liquid tokens, and take advantage of the benefits that liquid staking offers.
FAQs on Liquid Staking
1. **What is the difference between traditional staking and liquid staking?**
Traditional staking involves locking up your tokens to support network operations, while liquid staking provides a tradable
token in return for your staked assets, allowing you to maintain liquidity and flexibility.
2. **Is liquid staking safe?**
While the safety of liquid staking varies depending on the platform, it is generally considered secure. However, always do your research and choose a reputable platform before staking your assets.
3. **Do I still receive staking rewards with liquid staking?**
Yes, one of the benefits of Liquid Staking is that you continue to receive staking rewards while enjoying the added benefits of liquidity and flexibility.
4. **Can I stake any cryptocurrency using liquid staking?**
Not all cryptocurrencies support liquid staking. It is primarily used for assets on PoS blockchains. Be sure to check if your chosen platform supports the specific asset you wish to stake.
5. **Are there any fees associated with liquid staking?**
Fees for liquid staking may vary depending on the platform. It's essential to research the fee structure before committing to a liquid staking solution.
6. **How do I un-stake my assets in liquid staking?**
To un-stake your assets, you'll typically need to exchange your liquid tokens back to the original tokens and then follow the un-staking process outlined by your chosen platform.
Conclusion
-----------
The benefits of Liquid Staking are clear: greater flexibility, increased liquidity, risk mitigation, and more inclusive opportunities for smaller investors. With these advantages, it's no surprise that liquid staking is revolutionizing the digital asset management landscape. By understanding the ins and outs of this innovative solution, you'll be well-equipped to unlock the full potential of your digital assets and enhance your investment experience. By introducing a liquid, tradable token in exchange for staked assets, it enhances the staking experience and unlocks a world of new opportunities for investors, traders, and the broader DeFi ecosystem.
(1) What is Liquid Staking? Platforms, Tokens, Risks and Benefits. https://blog.changehero.io/liquid-staking-guide/.
(2) Liquid Staking Definition | CoinMarketCap. https://coinmarketcap.com/alexandria/glossary/liquid-staking.
(3) What is liquid staking and how does it work? | Finoa. https://www.finoa.io/blog/guide-liquid-staking/.
(4) Everything you need to know about Liquid Satking. https://www.staderlabs.com/blog/staking-basics/what-is-liquid-staking/
(5) Liquid Staking: Crypto’s New Phantom Money Machine - Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/digital-assets/2023/05/03/liquid-staking-cryptos-new-phantom-money-machine/.
The Convergence of Bitcoin and AI: How Crypto Can Fuel Autonomous Agents
 TL;DR
TL;DR
- Ark Invest's video interview explores the synergy between Bitcoin and AI.
- Key aspects like decentralization, transparency, and security are foundational to both.
- AI enhances Bitcoin's security, efficiency, and accessibility.
- Bitcoin's blockchain technology promises to make AI more secure and transparent.
- Challenges include regulatory hurdles and low adoption rates.
- Future prospects lie in Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) and AI-driven Bitcoin economies.
The worlds of Bitcoin and artificial intelligence (AI) are rapidly converging, with major implications for the future of automation, work, and decentralized finance. In this in-depth article, we'll explore how Bitcoin and blockchain technology are powering a new wave of AI applications and autonomous agents.
Introduction: The Bitcoin Brainstorm Podcast
This article summarizes key insights from a recent podcast hosted by Bitcoin Park, a Nashville campus focused on grassroots Bitcoin adoption, in partnership with ARK Invest, a leading investment manager focused on disruptive innovation.
The podcast brought together experts from both the Bitcoin and AI worlds, including:
- Frank Downing, Director of Research at ARK Invest
- Paul LeTort, CEO of Stackwork
- Lalu "Roastbeef" Joseph, CTO and Co-Founder of Lightning Labs
- Cody Lowe, Head of Developer Support at Anthropic
- Cathie Wood, Founder, CEO and CIO at ARK Invest
- Rodolfo Novak, Co-Founder of Bitcoin Park
The wide-ranging discussion provided critical insights on how these two rapidly evolving technologies can reinforce each other, potentially transforming finance, work, automation and more.
The Rise of Generative AI
A major theme was the rise of generative AI tools like DALL-E, GPT-3 and ChatGPT. Frank Downing explained how these models allow AI to create brand new content, from text to images to code, instead of just predicting outcomes.
The cost to train and run these complex models has declined exponentially. Back in 2020, training GPT-3 cost $4.6 million. Today, an equivalent model can be trained for under $450,000.
ARK believes generative AI could boost global productivity by embedding intelligence into software. Tools like GitHub Copilot already help developers write code 50% faster. By 2030, AI may be integrated into virtually all software, like the internet today.
As costs continue falling, access will spread. Bitcoin's low-fee micropayments can accelerate this democratization by enabling pay-per-use model for AI.
Lightning Is Fueling a New Wave of AI Applications
A key theme was how Bitcoin's Lightning Network is fueling a new wave of AI applications and business models.
Lightning offers instant, global payments for fractions of a penny. This unlocks "pay per use" model for AI APIs. Users can pay tiny amounts each time they query an AI model instead of a large monthly fee.
Developers like Roastbeef shared tools like l402 and Aperture that allow attaching Lightning payments to regular API calls.
For example, a natural language API could charge per token, rather than a fixed monthly rate. This aligns costs closely with usage.
Coders are already using these tools to monetize AI models. Someone could run a processor in their home and sell AI inferences for satoshis.
Lightning enables models to go global instantly, without needing credit cards or bank accounts. This helps spread AI to emerging markets.
Bitcoin Is Ideal for AI Providers
For businesses running AI models, Bitcoin provides major advantages over credit cards:
No Chargebacks: Once paid via Lightning, transactions are irreversible. This eliminates costly payment fraud and chargebacks.
Usage Based Billing: Lightning enables precise, per-query billing aligned with compute costs.
Global Reach: Lightning payments accessible to anyone, expanding market for AI companies.
These benefits incentivize AI providers to integrate Bitcoin payments. Tools from Lightning Labs make adoption easy.
Training AI Models with Bitcoin Incentives
Bitcoin also enables new models for sourcing training data and labeling datasets:
- Developers can pay crowd workers in real time via Lightning to label data, transcribe audio, etc.
- Bounties via platforms like Kaggle allow incentivizing specific datasets.
- Source data from users and pay via Lightning invoices.
Paying data contributors in Bitcoin taps into a global pool of participants and aligns incentives. This can massively scale the data needed to train algorithms.
Autonomous Agents with Bitcoin Wallets
Perhaps the most sci-fi application is autonomous software agents with Bitcoin wallets.
Developers can use tools like Langchain to build agents that can take actions via APIs. With Lightning, these agents can hold and spend Bitcoin.
This gives agents greater autonomy. They can purchase resources like cloud computing, data or human work as needed to complete tasks.
For example, an agent could:
- Hold a Bitcoin balance from its creator
- Analyze a task to determine required resources/skills
- Post bounties on StackWork requesting human assistance
- Pay for GPU processing from an AI API
- Rent server capacity as needed
- Purchase more Bitcoin when funds run low
This convergence between AI, Lightning and smart contracts enables increasingly sophisticated and automated agents.
Knowledge Work in the Age of AI
The podcast explored how AI may transform knowledge work and human roles. AI analyst Paul LeTort noted how tools like LLaMA now allow "everyone to have their own personal fleet of experts".
As AI assumes routine tasks, humans can focus on higher reasoning, creativity and emotional intelligence. Tech like Lightning enables selling specialized, human skills to a global market.
Work may shift to managing networks of narrow AI and human experts on demand. Specialized AIs can pay other AIs using Bitcoin - enabling an automated machine economy.
Bitcoin + AI = Explosive Growth Potential
ARK Invest founder Cathie Wood summed up the incredible potential from combining two S-curve technologies like Bitcoin and AI. Both are gaining momentum and entering a phase of explosive growth.
Just as the convergence between robots, energy storage and AI enabled companies like Tesla, the links between Bitcoin's decentralized finance and AI create huge opportunities.
As AI resources become globally accessible via Lightning payments, we may see a surge in startups and applications. This could rapidly scale Bitcoin adoption while accelerating AI productivity gains.
Conclusion: Democratization and Alignment
In summary, Bitcoin and AI exhibit a powerful synergy. Lightning payments make generative models accessible to more users worldwide. This helps democratize benefits from AI breakthroughs.
For coders and companies, Bitcoin provides incentives and revenue models that better align with AI systems. The ability to pay and be paid at the level of individual queries unlocks new economies.
As thought leaders recognize these trends, we'll continue to see accelerating convergence between blockchain and AI. With the right architecture, these technologies can combine to create an abundant, prosperous future.
This article only scratched the surface of concepts discussed in the podcast. To dig deeper, check out the show notes page for resources on Lightning, Langchain, autonomous agents and more.
See full video interview below:
Supplemental Info:
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin represents the original cryptocurrency - a completely digital form of money secured by cryptography and decentralized computing. It was created in 2009 by the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto, whose true identity remains unknown.
Some key properties of Bitcoin include:
- Decentralization - No central authority controls Bitcoin. It relies on distributed nodes that maintain the blockchain ledger. This contrasts with traditional finance, which relies on central banks and commercial banks.
- Transparency - The Bitcoin blockchain is public for anyone to view. All transactions are visible, enabling public verifiability. User identities are pseudonymous.
- Security - Bitcoin utilizes public key cryptography and proof-of-work mining to make transactions virtually tamper-proof. This enables trustless, peer-to-peer electronic cash.
- Fixed Supply - Only 21 million Bitcoins will ever exist. The code enforces hard scarcity that cannot be altered. This provides protection from inflation.
- Permissionless - Anyone can download Bitcoin software and participate without seeking approval from gatekeepers. Censorship of certain users is difficult.
Bitcoin functions as both a store of value and a payment network. It represents true digital gold - a provably scarce asset tradable anywhere in the world without intermediaries. As a payment rail, it allows fast value transfer without relying on centralized institutions.
What is AI?
Artificial intelligence refers to computational techniques that enable machines to exhibit qualities associated with human cognition - such as reasoning, learning, problem solving and pattern recognition.
AI research dates back to the 1950s, but has seen major advances in recent decades thanks to cheap computing power. Some common categories of AI include:
- Machine Learning - Algorithms that can improve and "learn" from data without explicit programming. Common methods include neural networks, deep learning and regression analysis.
- Computer Vision - Image recognition technology that allows computers to identify and understand visual content. Uses include facial recognition, medical imaging and self-driving vehicles.
- Natural Language Processing - The ability to parse, understand and generate human language. Enables chatbots, text summarization and sentiment analysis.
- Robotics - Mechanical systems capable of sensing, processing and taking physical actions such as assembly line manufacturing.
- Expert Systems - Programs encoding specialized human knowledge to provide advice or automation. This includes medical diagnosis tools and financial robo-advisors.
While general artificial intelligence does not yet exist, today's AI excels at narrow tasks by leveraging massive datasets. As algorithms grow more advanced, they are gradually automating a wider range of human activities.
How Bitcoin and AI are Related
Bitcoin and AI may seem totally unrelated at first glance. Cryptography, decentralized networks, and machine learning hail from very different domains. However, innovations in one field are increasingly influencing breakthroughs in the other.
There are both concrete connections and more philosophical synergies between blockchain and AI:
AI Improves the Security of Bitcoin
Sophisticated machine learning algorithms can boost security for Bitcoin users and infrastructure. Examples include:
- Detecting fraudulent account activity and unusual transactions - just like a credit card provider spots suspicious charges.
- Identifying and blocking harmful IP addresses engaging in spam or denial of service attacks.
- Pattern recognition to catch sybil attacks where one entity mimics multiple users.
- Neural networks that detect money laundering behavior within wallet interactions.
- Image recognition for enhanced identity verification when exchanging into local currency.
Overall, AI and machine learning provide enhanced pattern recognition and predictive abilities to blockchain networks. This strengthens defenses against malicious actors.
AI Enhances the Efficiency of Bitcoin
AI can optimize and streamline certain Bitcoin processes to increase overall efficiency. Use cases include:
- Predictive analytics to reduce blockchain congestion and speed up transaction clearing times - especially during periods of peak demand.
- Programmatic cryptocurrency trading driven by machine learning algorithms to maximize returns.
- Using past transaction data to model fees and recommend optimal fee levels to users.
- Chatbots and virtual assistants that allow easy access to account info or initiating payments via voice commands.
- Algorithmic optimizations such as AI-assisted mining software.
Together, these applications of AI make Bitcoin faster, more profitable, and simpler to use for everyday people.
AI Makes Bitcoin More Accessible
AI also serves to improve accessibility in the traditionally complex domain of cryptocurrencies. Some examples:
- Chatbots on exchanges simplifying the buying process for new users.
- Predictive typing and autocorrect for Bitcoin addresses and wallet passwords.
- Voice-activated applications enabling hands-free Bitcoin transactions.
- Smartphone apps leveraging biometrics like face ID or fingerprint scanning for easy onboarding.
- Automating the identity verification steps when exchanging Bitcoin into fiat currency.
- "Explainable AI" to interpret complex blockchain data for novices, from mempool congestion to DeFi investment strategies.
AI Helps in Automating Bitcoin Transactions
Smart contracts are programs stored on blockchains that run automatically when conditions are met. AI can enhance the capabilities of smart contracts and enable advanced automation. Use cases include:
- Algorithmic trading bots that buy/sell Bitcoin based on market indicators.
- AI advisors configuring custom smart contracts without human intervention.
- Automated execution of routine transactions, like contract settlements or loan payments.
- Smart appliances paying small amounts of Bitcoin to refill energy usage or data limits.
- Autonomous AI agents transacting Bitcoin to accomplish goals, described more below.
Together with IoT integration, AI and smart contracts can automate wide classes of routine financial transactions. This reduces reliance on manual processes. Bitcoin's natively digital nature makes it ideal for programmatic applications.
Ways Bitcoin and AI Could Benefit Each Other
Beyond specific connections, Bitcoin and AI each enable capabilities that could profoundly advance the other field:
AI Can Help Bitcoin Reach Its Potential
Bitcoin faces adoption hurdles and technical challenges that artificial intelligence may help overcome:
- Stability - High volatility inhibits mainstream adoption. Predictive analytics using AI could help stabilize prices and reduce large fluctuations.
- Complexity - The average person still finds cryptocurrency daunting. AI simplification tools help onboard new users.
- Efficiency - Slow transaction times have hindered adoption. AI optimization improves blockchain efficiency.
- Security - As Bitcoin scales, new attack vectors arise. AI pattern recognition fortifies defenses.
In short, AI provides enhanced analytics and automation that empower Bitcoin to fulfill its destiny as a global, decentralized financial system.
Bitcoin Could Revolutionize AI
On the flip side, Bitcoin's decentralized architecture offers advantages that could transform AI:
- Secure data - Blockchains enable robust data provenance and verification critical for training AI responsibly.
- Decentralized models - Distributing AI model training across nodes makes systems more robust and censorship-resistant.
- Accountability - Payment tracking on public ledgers creates transparency and accountability for AI.
- Accessibility - Micropayments allow affordable pay-per-use AI services reachable by anyone globally.
In essence, blockchain aligns AI incentives towards transparency while providing the data integrity and payment rails needed for equitable access.
Challenges Facing Bitcoin and AI Convergence
While the opportunities are tremendous, integrating Bitcoin and AI also involves significant hurdles:
Regulatory and Legal Issues
Government policies around cryptocurrency and data privacy present challenges including:
- KYC/AML - Know-your-customer and anti-money laundering regulations require user identity verification that compromises aspects of Bitcoin's anonymity and decentralization.
- Taxation - Cryptocurrency tax policies are still developing, creating uncertainty. AI and automation could end up highly taxed.
- Data Rights - Laws around data ownership, privacy and algorithmic transparency continue evolving. This may restrict AI applications.
- Smart Contract Enforceability - The legal standing of decentralized smart contract outcomes is still being established.
- AI Responsibility - Who is liable when autonomous AI causes harm? This must be addressed.
Ongoing legal clarification and prudent governance will be critical to realizing the potential of Bitcoin and AI safely and equitably.
Low Consumer Adoption Rates
While growing quickly, Bitcoin and AI remain at low adoption rates among the general public. Barriers include:
- Perceived Risk - Many consumers still view crypto as speculative and AI as untrustworthy.
- Lack of Understanding - The underlying technology is often poorly understood by non-experts.
- Usability Issues - Mainstream products still have UX issues and learning curves.
- Inertia - Overcoming established habits and financial systems creates friction.
Education, improved interfaces and demonstrated benefits will be key to driving mass acceptance of blockchain and algorithmic systems.
Conclusion
The convergence of Bitcoin and artificial intelligence represents an incoming tsunami transforming finance, data, automation and potentially society as a whole. These decentralized and algorithmic technologies exhibit a deep synergy, with innovations in one domain rapidly accelerating progress for the other.
Key insights include:
- Bitcoin and AI strongly complement each other on both a practical and philosophical level. Their integration can produce capabilities exceeding the sum of their parts.
- AI can boost Bitcoin's security, efficiency and accessibility - helping it reach its ambitions as decentralized global money.
- Bitcoin's architecture offers data integrity, transparency and micropayments that could profoundly advance AI safety and equity.
- Major regulatory, adoption and usability hurdles must still be overcome to realize this combined potential.
The path forward promises to be challenging yet immensely rewarding if we collectively navigate it with wisdom. As financial and knowledge systems grow increasingly decentralized and automated, the interfaces between humans, algorithms and blockchains will become the next frontier.
The Institutional Roadmap: Decrypting Cycles and Trends in Digital Asset Markets
 TL;DR
TL;DR
- Cryptocurrencies go through predictable boom-bust cycles of accumulation, markup, distribution, and markdown phases.
- Analyzing historical precedents shows the high volatility across crypto cycles.
- Market psychology and investor behavior drive cycle extremes based on fear, greed, and confusion.
- Fundamental factors like technology, adoption, regulations, economics, and manipulation also influence cycles.
- Institutions should develop strategies aligned to each phase, including long-term holding, dollar-cost averaging, technical/fundamental analysis, diversification, and risk management.
- Thoughtful regulations can facilitate institutional investment and dampen cycle volatility over time.
Introduction
Cryptocurrencies have experienced tremendous growth over the past decade, evolving from niche technology into a mainstream financial asset class. As institutional investors enter this nascent market, it is crucial to understand the cyclical nature of cryptocurrencies and how to effectively navigate the various phases. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of crypto market cycles, historical precedents, driving factors, and strategies for institutional investors.
The Importance of Understanding Crypto Cycles
- Risk Mitigation - The high volatility of cryptocurrencies poses significant risks. Analyzing cycles enables effective hedging and protection against the downside.
- Optimal Entry Points - Identifying cycle lows provides ideal opportunities to enter positions before the next markup phase.
- Optimal Exit Points - Selling near cycle tops allows maximizing returns before prices decline.
- Portfolio Diversification - Cryptocurrencies have low correlations with traditional assets and can enhance portfolio returns.
The Four Phases of a Cryptocurrency Market Cycle
Cryptocurrency markets tend to undergo four distinct phases:
Accumulation Phase
- Prices are low and stagnant after a prior markdown phase.
- Trading volumes are low.
- Only informed investors are actively accumulating.
- Media and retail interest remain indifferent.
Markup Phase
- Prices start trending higher.
- Trading volumes increase substantially.
- Media coverage intensifies, fueling retail FOMO.
- Market sentiment shifts to optimism.
Distribution Phase
- Prices reach a cycle peak and start to stagnate.
- Trading volumes remain high but start declining.
- Informed investors begin distributing holdings.
- Market sentiment turns cautious and confused.
Markdown Phase
- Prices collapse rapidly as panic selling sets in
- High volatility and capitulation selling wipe out gains
- Media coverage focuses on negativity and risks
- Market sentiment turns extremely pessimistic
|
Phase |
Investor Behavior |
Market Sentiment |
|
Accumulation |
Buying |
Indifferent |
|
Markup |
Holding |
Optimistic |
|
Distribution |
Selling |
Mixed |
|
Markdown |
Panic Selling |
Pessimistic |
Historical Cycles in Leading Cryptocurrencies
Analyzing historical price charts offers critical insights into crypto market cycles:
Bitcoin Cycles

Bitcoin, the pioneer cryptocurrency, drives the crypto market cycles and has seen several cycles since its 2009 inception. Its price journey from mere cents to tens of thousands of dollars exemplifies the power of these cycles. For instance, Bitcoin's massive 2017 surge and subsequent 2018 crash were followed by similar cycles in 2020-2021. You can view this data on CoinMarketCap, in addition to the following:
- 2011 Bubble - Price rose from $0.30 to $32 before collapsing to $2
- 2013 Rally - Bottomed at $65 and peaked at $1,150 before declining 84% (Hayes, 2018)
- 2017 Mania - Surged from $1,000 to nearly $20,000 before plunging over 80% (Corbet et al., 2020)
- 2020-2021 Bull Run - Gained over 1,000% from lows of $3,800 to highs of $69,000 (Bartos, 2016)
Ethereum Cycles
Ethereum as the second-largest crypto has experienced similar bubble-crash cycles:
- 2017 Irrational Exuberance - Spiked from $8 to $1,400 before diving 94%
- 2018 Bear Market - Fell from $1,400 to below $100 over 12 months
- 2020-2021 Bull Run - Skyrocketed from $100 to above $4,000 for 4,000% gains (Baur et al., 2018)
These examples illustrate the dramatic price swings across crypto adoption cycles. Grasping this volatile, cyclical pattern is key for institutional investors.
Market Psychology and Investor Behavior
Extreme emotions and irrational investor behavior significantly impact crypto market cycles, especially during later stages:
Greed and FOMO
The markup phase is driven largely by greed and FOMO as prices skyrocket. Retail investors flock in, inflating the bubble.
Fear and Panic
The markdown phase sparks fear and panic selling, driving a capitulation crash. Weak hands sell at substantial losses.
Confusion
The distribution phase creates confusion as the exuberance wanes. Investors are unsure whether to hold or sell.
Understanding and accounting for emotional factors allow institutions to avoid irrational decisions.
Fundamental Drivers of Crypto Market Cycles
Along with investor psychology, several fundamental factors contribute to the ebbs and flows of crypto cycles:
Technological Innovation - Key advancements like Taproot, EIP-1559, and the Merge catalyze investor interest and markups.
Mainstream Adoption - Growing integration of cryptocurrencies into financial services spurs investor demand.
Regulatory Changes - Increased oversight can deter investment, while clarity catalyzes markups.
Macroeconomics - Issues like inflation and economic instability encourage the adoption of cryptocurrency as a hedge.
Market Manipulation - Coordinated price actions by large holders ("whales") exaggerate cycle highs and lows.
Tracking Major Trends Reshaping Digital Asset Markets
The crypto landscape is constantly evolving, driven by transformative trends:
|
Trend |
Tech Project |
Potential Impact |
|
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) |
New Yield Farming Platforms |
Increased user adoption & institutional interest |
|
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) |
Cutting-edge NFT marketplaces |
Rise in digital asset value & the creative economy |
|
Real-World Blockchain Apps |
New supply chain solutions |
Sustainability-focused investments & supply chain transparency |
|
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs |
Government-backed digital forms of fiat currency |
Compete against private sector stable coins in marketplace transactions. |
What factors affect transitions between crypto market cycle phases?
Several key factors drive the shifts between different phases of the crypto market cycle:
- Investor psychology - Greed, fear, confusion, and optimism among market participants propel transitions between euphoria and capitulation.
- Market events - Exchange hacks, new regulations, major protocol upgrades, or other events spark price movements between phases.
- Adoption and fundamentals - Growing development activity, institutional involvement, and real-world usage drive markets into new accumulation phases.
- Media hype - Intense news coverage of crypto pushes markets into overbought conditions ripe for distribution.
- Macroeconomics - Issues like inflation, economic instability, or geopolitical crises encourage flows into crypto assets.
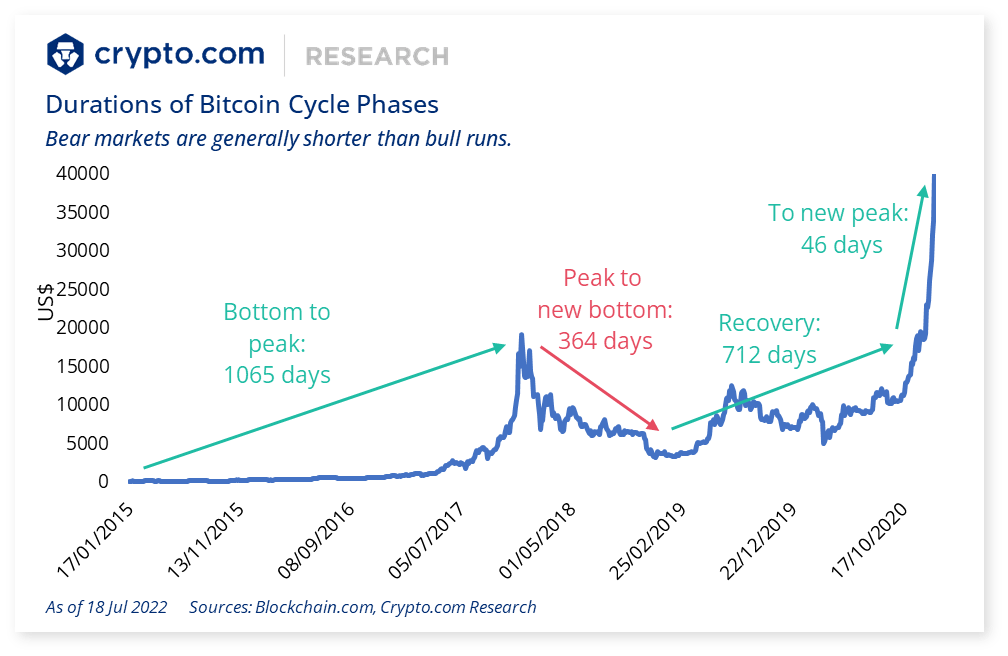
Developing Strategies to Identify Emerging Trends Early
Succeeding in crypto's volatility requires identifying major trends early. Key strategies include:
- Understanding investor psychology to predict sentiment shifts based on behavior.
- Monitoring technological innovations like new cryptocurrencies, DeFi platforms, and NFT marketplaces.
- Analyzing a trend's trajectory to determine optimal entry and exit points.
However, market sentiment could be an even bigger influence. A few examples:
|
Influencer |
Description |
|
Elon Musk |
Tweets have caused significant price swings in Bitcoin and Dogecoin. |
|
China's Government |
Policies affecting mining have created massive ripples in crypto markets. |
|
Coinbase Listing |
A listing on this top exchange typically results in a price surge for that cryptocurrency. |
Managing Volatility Through Analytical Approaches
Cryptocurrencies' extreme volatility demands robust analytical strategies:
- Risk management via diversifying into different crypto assets.
- Using analytics tools for data-driven decision making.
- Tracking influencers like Elon Musk and China policies that trigger price movements.
- Evaluating blockchain fundamentals to identify promising long-term projects.
Constructing a Balanced Cryptocurrency Portfolio
Strategic portfolio construction is vital to mitigate volatility risks:
- Major coins like Bitcoin and Ethereum are relatively safe bets.
- Allocations to promising altcoins and new ICOs for higher growth.
- Constant research to identify opportunities based on trends and innovations.
Implications and Strategies for Institutional Investors
The cyclical crypto markets require institutions to develop robust strategies tailored to each phase:
Long-term Holding
- Holding through cycles mitigates risks from short-term volatility.
- Allows capturing full upside potential over multiple years.
Dollar-Cost Averaging
- Phases purchases over extended periods to reduce market timing risks.
- Especially effective for accumulating during markdowns and distributions.
Technical Analysis
- Identify support, resistance, trends, and patterns to optimize entries and exits.
- Useful for timing cycle lows and highs.
Fundamental Analysis
- Assess project roadmaps, adoption metrics, and partnerships for intrinsic value insights.
- Helps value cryptocurrencies through hype and bearishness.
Portfolio Diversification
- Cryptocurrencies have low correlation to stocks and bonds.
- Strategic allocation dampens portfolio volatility and enhances returns.
Active Risk Management
- Hedge excessive risks using derivatives like options contracts.
- Set stop losses to protect against severe markdowns.
The Regulatory Landscape
Given cryptocurrencies' expansive growth, regulators worldwide are attempting to develop frameworks to provide oversight without hindering innovation. However, significant uncertainties remain:
- While the SEC, CFTC, and IRS have provided some guidance, lack of clear regulations in the US fosters confusion. The Biden administration has signaled apathy and potential hostility towards crypto innovation.
- Major economies like the EU, Japan, and South Korea are progressing in crafting balanced regulations. However, fragmented cross-border policies risk hampering global adoption.
- Stricter KYC and AML policies do improve legitimacy, but over-regulation risks driving activity underground. Policymakers must strike a prudent balance.
- Tax treatment definitions enable proper accounting but remain inconsistent across jurisdictions. Unclear tax policies suppress fuller institutional investment.
Overall, the global regulatory outlook remains murky. While thoughtful crypto regulations could facilitate institutional participation and financial stability, misguided policies driven by incumbent interests threaten technological progress and mainstream adoption. Institutions must actively engage with lawmakers to advocate for innovation-friendly frameworks. Without rational, future-focused policies, regulators risk severely undermining cryptocurrencies' paradigm-shifting potential.
Implications for Institutional Investors
Understanding crypto cycles can significantly reduce risk and offer high returns. Here are some strategies and pitfalls to avoid:
Strategies
- Long-term Holding: Helps mitigate short-term volatility.
- Technical Analysis: Utilize charts and patterns for decision-making.
- Fundamental Analysis: Focus on the intrinsic value of the asset.
Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-leveraging: Excessive use of leverage can amplify losses.
- Ignoring Regulations: Regulatory changes can abruptly alter market dynamics. Stay updated with SEC announcements.
- Lack of Diversification: Over-concentration in a single asset is risky.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrencies are a game-changer in finance but come with high volatility and cycles. For institutional investors, it's crucial to have strategies tailored to these cycles. By combining smart strategies, proper asset allocation, and risk management, cryptocurrencies can be an asset for institutional portfolios. The long-term view is positive as adoption grows in finance and global trade.
Key Takeaways on Crypto Market Cycles
- The crypto market cycle has four distinct phases: accumulation, markup, distribution and markdown.
- Factors like investor psychology, major events, adoption, media hype and macroeconomics drive transitions between different phases.
- Tailoring trading strategies to each phase can maximize gains and minimize losses.
- Understanding crypto investor psychology allows avoiding emotional decision-making pitfalls.
- Experience and learning across market cycles refines strategy and psychology for improved results.
Joining a DAO: Investor Pros and Cons
TL;DR:
- What is a DAO?: A Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) is a blockchain-based entity governed by smart contracts and its token holders. It operates autonomously, decentralizes decision-making, and offers democratic governance.
- Why Join a DAO: DAOs offer multiple income streams like staking and yield farming. They provide token holders with governance power and are at the forefront of blockchain innovation.
- Institutional Involvement: As of June 2021, over $1 billion has been invested in DAOs. Institutions are not just investing but also participating in venture DAOs, providing value-add services, and even creating new financial products like "CryptoIRAs."
- Risks and Challenges: Be cautious of regulatory risks, potential smart contract bugs, and the complexity and volatility of DAO tokens.
- Choosing and Investing: Before joining a DAO, research its whitepaper, governance, and community. Diversify your investment, understand your risk tolerance, and have an exit strategy.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are drawing individual and institutional investors in the crypto ecosystem. As with any investment, DAOs have perks and cons. This article covers all you need to know before entering the DAO pool.
Understanding Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
A DAO is a blockchain-based entity governed by smart contracts and consensus among its token holders. These organizations are:
- Autonomous: After deployment, the DAO operates independently, requiring no human oversight.
- Decentralized: Decision-making is spread across all token holders, avoiding central points of failure.
- Democratic: DAOs use tokens to grant give voting rights, ensuring that all decisions are made collectively.
Why DAOs Are Transformative
DAOs are not only a technological advancement, but also a social experiment and a new organizational structure. For example, they can automate financial processes and decision-making, providing a level of transparency that is difficult to find in conventional businesses.. According to 101 Blockchains, these features make DAOs both intriguing and complex entities.
Benefits of Joining a DAO as an Investor
Financial Incentives
DAOs offer multiple streams of potential income. You can earn through staking, yield farming, or even by participating in decision-making processes that lead to profitable outcomes. These financial incentives are often laid out in the DAO's whitepaper, providing a detailed understanding of potential returns.
Governance Power
Owning tokens gives you access to governance rights in addition to financial advantages. According to Cointelegraph, this token-based governance model provides a decentralized and democratic way to steer the organization's future.
Transparency and Innovation
Every transaction and vote within a DAO is recorded on the blockchain, providing an unprecedented level of transparency. As Investopedia points out, this ensures that you can audit the organization's activities at any time. Additionally, DAOs often spearhead innovations like decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Giving members access to projects early in development.
|
Pros |
Explanation |
| Financial Incentives | Earn passive income through staking, yield farming, etc. |
| Governance Power | Influence the DAO's direction with your votes. |
| Transparency | All actions are public and auditable. |
| Innovation | Be part of groundbreaking projects. |
Institutional Involvement in DAOs
As of June 2021, more than $1 billion has been invested in DAOs, and institutional investors are a significant part of this landscape. Here's how they're getting involved:
Direct Investment
Institutions, particularly venture capitalists, are investing heavily in DAOs. They understand the paradigm shift that DAOs represent and are willing to back it with significant capital, as mentioned in this Blockworks report.
Venture DAOs
These are specialized DAOs focused on raising and investing capital. According to Cointelegraph, institutional investors are actively participating in these DAOs by contributing funds and voting on key decisions.
Value-Add Services
While the financial backing from institutional investors can provide immediate liquidity and operational runway for DAOs, the influence of these institutions extends far beyond mere capital investment. They bring a wealth of specialized services and expertise that can serve as pivotal growth catalysts for DAOs. Let's explore some of the areas where this institutional expertise becomes invaluable.
- Strategic Guidance and Mentorship
Institutional investors often have years, if not decades, of experience in business strategy, market penetration, and scalability. This seasoned perspective can offer DAOs the mentorship and guidance needed to navigate through the complexities of growth and market positioning.
- Access to Networks and Partnerships
Institutions often have extensive networks across various industries. By becoming part of a DAO, they can facilitate strategic partnerships and collaborations, opening doors that might otherwise be challenging to access for a decentralized entity.
- Regulatory Compliance and Legal Support
One of the major hurdles for DAOs is the murky regulatory landscape in which landscape they operate within. Institutions often have legal teams well-versed in compliance, governance, and international law. This support can help DAOs interpret existing laws and prepare for potential future regulations, thereby reducing legal risks.
- Market Research and Data Analysis
Institutions often have resources dedicated to market research and data analytics. This data-driven approach can offer insights into consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive landscapes, empowering the DAO to make informed decisions.
- Technology and Security Audits
Institutions can also offer technical expertise, including security audits for smart contracts, which is crucial given that DAOs operate on blockchain technology. Ensuring the integrity and security of smart contracts can protect against hacks and vulnerabilities.
As Coindesk highlights, this multi-faceted expertise from institutions can significantly contribute to a DAO's growth and stability. It's not just about pumping money into the system; it's about elevating the entire ecosystem through value-added services and expertise.
Financial Products
Innovative financial products like "CryptoIRAs" are emerging to facilitate institutional investment in DAOs. Harvard Law's Corporate Governance blog discusses these products as a way to broaden the scope of DAO investments.
However, it's crucial to understand that traditional investors might still be skeptical about DAOs, primarily due to regulatory uncertainties and lack of central leadership.
Risks and Challenges of Investing in DAOs
Regulatory Risks
DAOs operate in a regulatory gray area, and an adverse legal decision can negatively impact your investment. This is a concern that many traditional investors share.
Smart Contract Risks
The functionality of a DAO hinges on the robustness of its smart contracts. A bug in the code can lead to financial losses, as was the case with the infamous DAO hack in 2016, which resulted in a loss of $50 million.
Volatility and Complexity
The value of DAO tokens can be highly volatile. Moreover, the complexity of DAOs, from governance mechanisms to utility features, requires a steep learning curve. TechTarget offers some insights into the intricacies of DAOs that every investor should understand.
Choosing the Right DAO and Developing an Investment Strategy
A strong community is often a good indicator of the DAO's health. It's also advisable to diversify your investments and understand your risk tolerance. And finally, have an exit strategy.
Before making an investment, dig deep into the DAO’s whitepaper, governance structure, tokenomics, and have a strong investment partner to help chart the path,path like Alpha Stake.
Conclusion
DAOs represent an evolution in how we think about organizations and governance. They offer unique benefits but also pose significant risks. If you're considering joining a DAO, arm yourself with as much knowledge as possible. This is a new frontier, and it pays to be well-prepared. Welcome to the future of investing!
People Also Asked
Can DAOs be Sued?
Yes, DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) can technically be sued, but the process is complex and largely uncharted territory. DAOs exist on blockchain networks and are not centralized entities, making it difficult to hold them legally accountable. However, if a DAO interacts with real-world assets or engages in activities that are illegal, the parties involved could potentially be sued.
Types of Lawsuits:
- Contractual Disputes
- Fraudulent Activities
- Regulatory Violations
Can DAOs be Regulated?
DAOs can be subject to regulation, but the regulatory landscape is still evolving. Different jurisdictions have different stances on how to regulate DAOs. In the U.S., for example, the SEC has shown interest in regulating DAOs that issue tokens resembling securities.
Regulatory Bodies:
- SEC (U.S.)
- FCA (UK)
- BaFin (Germany)
Are DAOs Legal Entities and What Types of DAOs Exist in 2023?
DAOs are not universally recognized as legal entities. However, in some jurisdictions, like Wyoming, USA, DAOs can be registered as LLCs.
Types of DAOs in 2023:
- Investment DAOs
- Service DAOs
- Social DAOs
- NFT DAOs
Does the DAO Need a Specific Corporate Location?
No, DAOs do not need a specific corporate location as they exist on a blockchain. However, for legal and tax purposes, some choose to register in jurisdictions that are crypto-friendly.
Popular Jurisdictions:
- Wyoming, USA
- Malta
- Switzerland
For How Long Does the DAO Intend to Exist?
The lifespan of a DAO is generally indefinite and exists as long as the blockchain it resides on exists. However, DAOs can be dissolved through governance proposals.
Factors Affecting Lifespan:
- Governance Decisions
- Regulatory Actions
- Market Conditions
How is DAO Membership to be Transferred?
DAO membership is usually tied to token ownership. Transferring tokens often equates to transferring membership. However, some DAOs have more complex membership requirements.
Transfer Methods:
- Peer-to-peer token transfer
- On-chain proposals
- Smart contract execution
What are the Various DAO Governance Challenges?
DAO governance faces several challenges, including voter apathy, centralization risks, and smart contract vulnerabilities.
Challenges:
- Voter Apathy
- Centralization Risks
- Smart Contract Flaws
What Rights Do DAO Smart Contract Members Have?
Rights vary depending on the DAO's governance model, but generally include voting on proposals and financial decisions.
Common Rights:
- Voting
- Proposal Submission
- Financial Participation
Why Do We Need DAOs?
DAOs offer a decentralized way to manage collective resources. They can be more transparent, democratic, and resistant to censorship compared to traditional organizations.
Benefits:
- Transparency
- Decentralization
- Innovation
Must a DAO Issue Tokens or Cryptocurrency?
No, issuing tokens or cryptocurrency is not a requirement for DAOs, although it's common. Tokens often serve as a governance tool and a way to incentivize participation.
Token Functions:
- Governance
- Incentivization
- Asset Management
In summary, DAOs are a groundbreaking innovation but come with their own set of legal and governance challenges. As the regulatory landscape evolves, we can expect more clarity on these issues.








